Distinct initiating events underpin the immune and metabolic heterogeneity of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31519898
- PMCID: PMC6744438
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12164-y
Distinct initiating events underpin the immune and metabolic heterogeneity of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
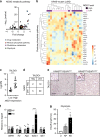
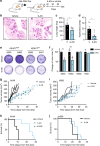
The KRAS oncoprotein, a critical driver in 33% of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), has remained an elusive clinical target due to its perceived undruggable nature. The identification of dependencies borne through common co-occurring mutations are sought to more effectively target KRAS-mutant lung cancer. Approximately 20% of KRAS-mutant LUAD carry loss-of-function mutations in KEAP1, a negative regulator of the antioxidant response transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2. We demonstrate that Keap1-deficient KrasG12D lung tumors arise from a bronchiolar cell-of-origin, lacking pro-tumorigenic macrophages observed in tumors originating from alveolar cells. Keap1 loss activates the pentose phosphate pathway, inhibition of which, using 6-AN, abrogated tumor growth. These studies highlight alternative therapeutic approaches to specifically target this unique subset of KRAS-mutant LUAD cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

