A thyroid hormone network exists in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients
- PMID: 31519956
- PMCID: PMC6744488
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49743-4
A thyroid hormone network exists in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients
Abstract
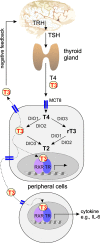
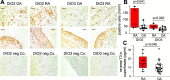
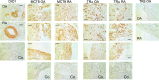
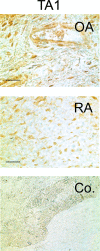
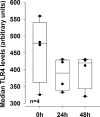
While patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) sometimes demonstrate thyroidal illness, the role of thyroid hormones in inflamed synovial tissue is unknown. This is relevant because thyroid hormones stimulate immunity, and local cells can regulate thyroid hormone levels by deiodinases (DIO). The study followed the hypothesis that elements of a thyroid hormone network exist in synovial tissue. In 12 patients with RA and 32 with osteoarthritis (OA), we used serum, synovial fluid, synovial tissue, and synovial fibroblasts (SF) in order to characterize the local thyroid hormone network using ELISAs, immunohistochemistry, imaging methods, tissue superfusion studies, cell-based ELISAs, flow cytometry, and whole genome expression profiling. Serum/synovial fluid thyroid hormone levels were similar in RA and OA (inclusion criteria: no thyroidal illness). The degradation product termed reverse triiodothyronine (reverse T3) was much lower in serum compared to synovial fluid indicating biodegradation of thyroid hormones in the synovial environment. Superfusion experiments with synovial tissue also demonstrated biodegradation, particularly in RA. Cellular membrane transporters of thyroid hormones, DIOs, and thyroid hormone receptors were present in tissue and SF. Density of cells positive for degrading DIOs were higher in RA than OA. TNF increased protein expression of degrading DIOs in RASF and OASF. Gene expression studies of RASF revealed insignificant gene regulation by bioactive T3. RA and OA synovial tissue/SF show a local thyroid hormone network. Thyroid hormones undergo strong biodegradation in synovium. While bioactive T3 does not influence SF gene expression, SF seem to have a relay function for thyroid hormones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Distinct serum and synovial fluid interleukin (IL)-33 levels in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2012 Jan;79(1):32-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.02.011. Epub 2011 Mar 26. Joint Bone Spine. 2012. PMID: 21441054
-
Differential inflammation-mediated function of prokineticin 2 in the synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with osteoarthritis.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 15;11(1):18399. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97809-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34526577 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of rhythms of molecular clocks in primary synovial fibroblasts of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, role of IL-1β/TNF.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 May 23;14(3):R122. doi: 10.1186/ar3852. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22621205 Free PMC article.
-
The metastasis associated protein S100A4: a potential novel link to inflammation and consequent aggressive behaviour of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Nov;67(11):1499-504. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.079905. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 18056757 Review.
-
Synovial Tissue: Cellular and Molecular Phenotyping.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019 Aug 29;21(10):52. doi: 10.1007/s11926-019-0858-1. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31468238 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in Thyroid Hormone Signaling Mediate Cardiac Dysfunction in the Tg197 Mouse Model of Arthritis: Potential Therapeutic Implications.J Clin Med. 2021 Nov 25;10(23):5512. doi: 10.3390/jcm10235512. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34884213 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep duration and the risk of new-onset arthritis in middle-aged and older adult population: results from prospective cohort study in China.Front Public Health. 2024 May 30;12:1321860. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1321860. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38873298 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydroepiandrostenedione sulphate (DHEAS) levels predict high risk of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in subclinical hypothyroidism.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 16;16(2):e0246195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246195. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33592022 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic evidence links hyperthyroidism to knee osteoarthritis.Hormones (Athens). 2025 Jun;24(2):359-365. doi: 10.1007/s42000-025-00648-0. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Hormones (Athens). 2025. PMID: 40183994 Free PMC article.
-
Selected musculoskeletal disorders in patients with thyroid dysfunction, diabetes, and obesity.Reumatologia. 2023;61(4):305-317. doi: 10.5114/reum/170312. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Reumatologia. 2023. PMID: 37745138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kerola AM, et al. Increased risk of levothyroxine-treated hypothyroidism preceding the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide registry study. Clin. Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32:455–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

