Early and Sustained Increases in Leukotriene B4 Levels Are Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome in Ischemic Stroke Patients
- PMID: 31520306
- PMCID: PMC7007445
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-019-00787-4
Early and Sustained Increases in Leukotriene B4 Levels Are Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome in Ischemic Stroke Patients
Abstract
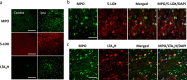
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) has been implicated in ischemic stroke pathology. We examined the prognostic significance of LTB4 levels in patients with acute middle cerebral artery (MCA) infarction and their mechanisms in rat stroke models. In ischemic stroke patients with middle cerebral artery infarction, plasma LTB4 levels were found to increase rapidly, roughly doubling within 24 h when compared to initial post-stroke levels. Further analyses indicate that poor functional recovery is associated with early and more sustained increase in LTB4 rather than the peak levels. Results from studies using a rat embolic stroke model showed increased 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) expression in the ipsilateral infarcted cortex compared with sham control or respective contralateral regions at 24 h post-stroke with a concomitant increase in LTB4 levels. In addition, neutrophil influx was also observed in the infarcted cortex. Double immunostaining indicated that neutrophils express 5-LOX and leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H), highlighting the pivotal contributions of neutrophils as a source of LTB4. Importantly, rise in plasma LTB4 levels corresponded with an increase in LTB4 amount in the infarcted cortex, thereby supporting the use of plasma as a surrogate for brain LTB4 levels. Pre-stroke LTB4 loading increased brain infarct volume in tMCAO rats. Conversely, administration of the 5-LOX-activating protein (FLAP) inhibitor BAY-X1005 or B-leukotriene receptor (BLTR) antagonist LY255283 decreased the infarct volume by a similar extent. To conclude, targeted interruption of the LTB4 pathway might be a viable treatment strategy for acute ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Ischemic stroke; animal models; leukotriene B4; middle cerebral artery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Time-related changes in myeloperoxidase activity and leukotriene B4 receptor binding reflect leukocyte influx in cerebral focal stroke.Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1995 Jan;24(1):13-30. doi: 10.1007/BF03160109. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1995. PMID: 7755844
-
Leukotriene B4 costimulates 5-lipoxygenase activity in neutrophils via increased 5-lipoxygenase translocation.Am J Physiol. 1997 Apr;272(4 Pt 1):C1329-34. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1997.272.4.C1329. Am J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9142859
-
Reperfusion increases neutrophils and leukotriene B4 receptor binding in rat focal ischemia.Stroke. 1992 Sep;23(9):1337-47; discussion 1347-8. doi: 10.1161/01.str.23.9.1337. Stroke. 1992. PMID: 1381529
-
Biosynthesis of leukotriene B4.Semin Immunol. 2017 Oct;33:3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.07.012. Semin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29042025 Review.
-
[A Research on Drug Discovery for Intracerebral Hemorrhage Focusing on Leukotriene B4 and Its Receptor].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020;140(11):1323-1327. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.20-00145. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 33132267 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Plasma Resolvin D2 to Leukotriene B4 Ratio Is Reduced in Diabetic Patients with Ischemic Stroke and Related to Prognosis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 26;2021:6657646. doi: 10.1155/2021/6657646. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33728336 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multi-omic analysis of stroke recurrence in African Americans from the Vitamin Intervention for Stroke Prevention (VISP) clinical trial.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 4;16(3):e0247257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247257. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33661917 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lipids and Lipid Mediators Associated with the Risk and Pathology of Ischemic Stroke.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 20;21(10):3618. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103618. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32443889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Models to Investigate the Mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction on Inflammatory Injury Induced by Cerebral Ischemia.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jan 13;2021:2135394. doi: 10.1155/2021/2135394. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33519941 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Lipid Mediators Associate With Clinical Outcome After Successful Endovascular Thrombectomy in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 4;13:917974. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.917974. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35865524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peters-Golden M, Henderson WR., Jr Leukotrienes. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1841–54. - PubMed
-
- De Caterina R, Zampolli A. From asthma to atherosclerosis - 5-lipoxygenase, leukotrienes, and inflammation. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:4–7. - PubMed
-
- Di Gennaro A, Wågsäter D, Mäyränpää MI, Gabrielsen A, Swedenborg J, Hamsten A, Samuelsson B, Eriksson P, Haeggström JZ. Increased expression of leukotriene C4 synthase and predominant formation of cysteinyl-leukotrienes in human abdominal aortic aneurysm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:21093–7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

