Type I interferon and interferon-stimulated gene expression in oral epithelial cells
- PMID: 31520463
- PMCID: PMC7362904
- DOI: 10.1111/omi.12270
Type I interferon and interferon-stimulated gene expression in oral epithelial cells
Abstract
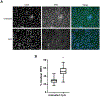
Oral epithelial cells (OEC) represent the first site of host interaction with viruses that infect the body through the oral route; however, their innate antiviral defense mechanisms yet to be defined. Previous studies have determined that OEC express pathogen-, damage-, or danger-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or DAMPs), but their expression of key antiviral innate immune mediators, including type I interferons (type I IFN) and interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) has not been studied extensively. We used the oral keratinocyte cell line, OKF6/TERT1, in the presence and absence of the viral mimics poly(I:C) and unmethylated CpG DNA, to define the expression of type I IFN and ISGs. We identified the basal expression of novel type I IFN genes IFNE and IFNK, while IFNB1 was induced by viral mimics, through the nuclear translocation of IRF3. Numerous ISGs were expressed at basal levels in OEC, with an apparent correlation between high expression and antiviral activity at the earlier stages of viral infection. Stimulation of OECs with poly(I:C) led to selective induction of ISGs, including MX1, BST2, PML, RSAD2, ISG15, and ZC3HAV1. Together, our results demonstrate that OECs exhibit a robust innate antiviral immune defense profile, which is primed to address a wide variety of pathogenic viruses that are transmitted orally.
Keywords: epithelial; innate immunity; interferon; interferon-stimulated gene; oral; virus.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

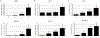
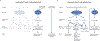
References
-
- Cervantes CAC, Oliveira LMS, Manfrere KCG, Lima JF, Pereira NZ, Duarte AJS, & Sato MN (2016). Antiviral factors and type I/III interferon expression associated with regulatory factors in the oral epithelial cells from HIV-1-serodiscordant couples. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 25875 10.1038/srep25875 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

