Factors predictive of the presence of a CSF1R mutation in patients with leukoencephalopathy
- PMID: 31520500
- PMCID: PMC6973227
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.14086
Factors predictive of the presence of a CSF1R mutation in patients with leukoencephalopathy
Abstract
Background and purpose: The purpose was to identify statistically factors that correlate with the presence of a colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) mutation and to reevaluate the accuracy of the current diagnostic criteria for CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy.
Methods: CSF1R testing was conducted on 145 consecutive leukoencephalopathy cases who were clinically suspected of having adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia. From these, 135 cases whose detailed clinical information was available were enrolled. Forward logistic stepwise regression was performed to generate a probability model to predict a positive CSF1R mutation result. The current diagnostic criteria were also applied to our cohort and their sensitivity and specificity were calculated.
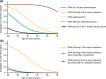
Results: Twenty-eight CSF1R-mutation-positive cases and 107 CSF1R-mutation-negative cases were identified. Our probability model suggested that factors raising the probability of a CSF1R-mutation-positive result were younger onset, parkinsonism, thinning of the corpus callosum and diffusion-restricted lesions. It also showed that involuntary movements and brainstem or cerebellar atrophy were negative predictors of a CSF1R-mutation-positive result. In our cohort, the sensitivity and specificity for 'probable' or 'possible' CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy were 81% and 14%, respectively.
Conclusions: Clinical and brain imaging features predictive of the presence of a CSF1R mutation are proposed. Consideration of these factors will help prioritize patients for CSF1R testing.
Keywords: adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia; colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor; diagnostic criteria; leukoencephalopathy; logistic regression.
© 2019 The Authors. European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lynch DS, Zhang WJ, Lakshmanan R, et al Analysis of mutations in AARS2 in a series of CSF1R‐negative patients with adult‐onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia. JAMA Neurol 2016; 73: 1433–1439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

