Lentivirus-mediated CDglyTK gene-modified free flaps by intra-artery perfusion show targeted therapeutic efficacy in rat model of breast cancer
- PMID: 31521130
- PMCID: PMC6744674
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-6111-5
Lentivirus-mediated CDglyTK gene-modified free flaps by intra-artery perfusion show targeted therapeutic efficacy in rat model of breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Free flap-mediated gene therapy in the tumor bed following surgical resection is a promising approach in cancer targeted treatment of residual disease. We investigated the selective killing efficacy of a lentivirus-mediated cytosine deaminase-thymidine kinase (CDglyTK) gene in transplanted breast cancer delivered into a free flap by intra-artery perfusion.
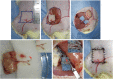
Methods: Proliferation, apoptosis, and cell cycle of rat SHZ-88 breast cancer cells transfected with a lentivirus-mediated CD/TK gene were measured following treatment with ganciclovir and 5-flucytosine in vitro. A model of residual disease of breast cancer in a rat superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) flap model was used to study the therapeutic potential of a double suicide CD/TK and prodrug system in vivo.
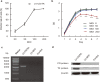
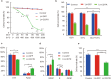
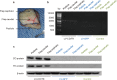
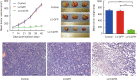
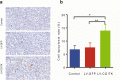
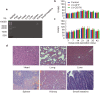
Results: Killing efficacy of the double suicide CD/TK and prodrug system on SHZ-88 cells was mediated by increased apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase with significant bystander effect. Following recombinant lentivirus transfection of rat SIEA flap by intra-artery perfusion, CD/TK gene expression was limited to the flap, and the volume and weight of transplanted tumors were significantly reduced without observable toxicity.
Conclusions: SIEA flaps transfected with a lentivirus-mediated CDglyTK gene by intra-artery perfusion effectively suppress transplanted breast tumor growth without obvious systemic toxic effects in rats.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CDglyTK gene; Free flap; Intra-artery perfusion; Lentiviral vector; Suicide gene therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenovirus-mediated tissue-targeted expression of the CDglyTk gene for the treatment of breast cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2012 Aug;6(2):321-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.925. Epub 2012 May 23. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 22641384
-
Lentivirus-mediated CD/TK fusion gene transfection neural stem cell therapy for C6 glioblastoma.Tumour Biol. 2013 Dec;34(6):3731-41. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0957-y. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23828263
-
[Targeted killing of colorectal tumor cells by lentiviral constructs containing CD/TK suicide genes and KDR promoter].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007 May;27(5):624-7. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17545072 Chinese.
-
Therapeutic potential of stem cells expressing suicide genes that selectively target human breast cancer cells: evidence that they exert tumoricidal effects via tumor tropism (review).Int J Oncol. 2012 Sep;41(3):798-804. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1523. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22736197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical development of retroviral replicating vector Toca 511 for gene therapy of cancer.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021 Sep;21(9):1199-1214. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2021.1902982. Epub 2021 May 6. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33724117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Delivery of cancer therapies by synthetic and bio-inspired nanovectors.Mol Cancer. 2021 Mar 24;20(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01346-2. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33761944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biologic Brachytherapy: Genetically Modified Surgical Flap as a Therapeutic Tool-A Systematic Review of Animal Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 25;25(19):10330. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910330. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang YS, Chen JL, Huang CS, Kuo SH, Jaw FS, Tseng YH, Ko WC, Chang YC. High mammographic breast density predicts locoregional recurrence after modified radical mastectomy for invasive breast cancer: a case-control study. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0784-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

