Characterization and risk association of polymorphisms in Aurora kinases A, B and C with genetic susceptibility to gastric cancer development
- PMID: 31521144
- PMCID: PMC6744709
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-6133-z
Characterization and risk association of polymorphisms in Aurora kinases A, B and C with genetic susceptibility to gastric cancer development
Abstract
Background: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes encoding mitotic kinases could influence development and progression of gastric cancer (GC).
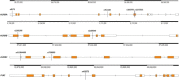
Methods: Case-control study of nine SNPs in mitotic genes was conducted using qPCR. The study included 116 GC patients and 203 controls. In silico analysis was performed to evaluate the effects of polymorphisms on transcription factors binding sites.
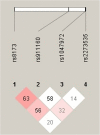
Results: The AURKA rs1047972 genotypes (CT vs. CC: OR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.05-3.65; p = 0.033; CC + TT vs. CT: OR, 1.94; 95% CI, 1.04-3.60; p = 0.036) and rs911160 (CC vs. GG: OR, 5.56; 95% CI, 1.24-24.81; p = 0.025; GG + CG vs. CC: OR, 5.26; 95% CI, 1.19-23.22; p = 0.028), were associated with increased GC risk, whereas certain rs8173 genotypes (CG vs. CC: OR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.36-0.99; p = 0.049; GG vs. CC: OR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.18-0.79; p = 0.010; CC + CG vs. GG: OR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.25-0.98; p = 0.043) were protective. Association with increased GC risk was demonstrated for AURKB rs2241909 (GG + AG vs. AA: OR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.01-2.56; p = 0.041) and rs2289590 (AC vs. AA: OR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.47-3.98; p = 0.001; CC vs. AA: OR, 6.77; 95% CI, 2.24-20.47; p = 0.001; AA+AC vs. CC: OR, 4.23; 95% CI, 1.44-12.40; p = 0.009). Furthermore, AURKC rs11084490 (GG + CG vs. CC: OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.04-2.81; p = 0.033) was associated with increased GC risk. A combined analysis of five SNPs, associated with an increased GC risk, detected polymorphism profiles where all the combinations contribute to the higher GC risk, with an OR increased 1.51-fold for the rs1047972(CT)/rs11084490(CG + GG) to 2.29-fold for the rs1047972(CT)/rs911160(CC) combinations. In silico analysis for rs911160 and rs2289590 demonstrated that different transcription factors preferentially bind to polymorphic sites, indicating that AURKA and AURKB could be regulated differently depending on the presence of particular allele.
Conclusions: Our results revealed that AURKA (rs1047972 and rs911160), AURKB (rs2241909 and rs2289590) and AURKC (rs11084490) are associated with a higher risk of GC susceptibility. Our findings also showed that the combined effect of these SNPs may influence GC risk, thus indicating the significance of assessing multiple polymorphisms, jointly. The study was conducted on a less numerous but ethnically homogeneous Bosnian population, therefore further investigations in larger and multiethnic groups and the assessment of functional impact of the results are needed to strengthen the findings.
Keywords: Cancer susceptibility; Chromosomal instability; Gastric cancer; Mitotic kinases; Single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tomonaga T, Nomura F. Chromosome instability and kinetochore dysfunction. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22:191–197. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

