Cultivation technology development of Rhodothermus marinus DSM 16675
- PMID: 31522265
- PMCID: PMC6801211
- DOI: 10.1007/s00792-019-01129-0
Cultivation technology development of Rhodothermus marinus DSM 16675
Abstract
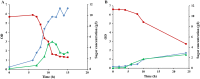
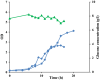
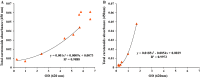
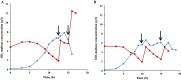
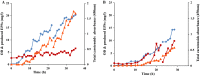
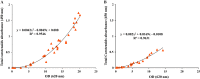
This work presents an evaluation of batch, fed-batch, and sequential batch cultivation techniques for production of R. marinus DSM 16675 and its exopolysaccharides (EPSs) and carotenoids in a bioreactor, using lysogeny broth (LB) and marine broth (MB), respectively, in both cases supplemented with 10 g/L maltose. Batch cultivation using LB supplemented with maltose (LBmalt) resulted in higher cell density (OD620 = 6.6) than use of MBmalt (OD620 = 1.7). Sequential batch cultivation increased the cell density threefold (OD620 = 20) in LBmalt and eightfold (OD620 = 14) in MBmalt. In both single and sequential batches, the production of carotenoids and EPSs using LBmalt was detected in the exponential phase and stationary phase, respectively, while in MBmalt formation of both products was detectable in both the exponential and stationary phases of the culture. Heteropolymeric EPSs were produced with an overall volumetric productivity (QE) of 0.67 (mg/L h) in MBmalt and the polymer contained xylose. In LB, QE was lower (0.1 mg/L h) and xylose could not be detected in the composition of the produced EPSs. In conclusion, this study showed the importance of a process design and medium source for production of R. marinus DSM 16675 and its metabolites.
Keywords: Bioreactor; Carotenoid; Exopolysaccharide; Rhodothermus marinus; Sequential batch cultivation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Medium development and production of carotenoids and exopolysaccharides by the extremophile Rhodothermus marinus DSM16675 in glucose-based defined media.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Oct 23;21(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01946-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36274123 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction provides insight into the metabolism of the thermophilic bacterium Rhodothermus marinus.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2025 Jan 7;101(1):fiae167. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiae167. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2025. PMID: 39716382 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the production of exopolysaccharides by two strains of the thermophilic bacterium Rhodothermus marinus.Carbohydr Polym. 2017 Jan 20;156:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.062. Epub 2016 Aug 21. Carbohydr Polym. 2017. PMID: 27842803
-
Characterization of carotenoids in Rhodothermus marinus.Microbiologyopen. 2018 Feb;7(1):e00536. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.536. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Microbiologyopen. 2018. PMID: 29045010 Free PMC article.
-
Production of extracellular bifidogenic growth stimulator (BGS) from Propionibacterium shermanii using a bioreactor system with a microfiltration module and an on-line controller for lactic acid concentration.J Biosci Bioeng. 2008 Mar;105(3):184-91. doi: 10.1263/jbb.105.184. J Biosci Bioeng. 2008. PMID: 18397766
Cited by
-
Engineering the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway in Rhodothermus marinus for lycopene production.Metab Eng Commun. 2020 Jul 28;11:e00140. doi: 10.1016/j.mec.2020.e00140. eCollection 2020 Dec. Metab Eng Commun. 2020. PMID: 32793416 Free PMC article.
-
Cultivation of the gut bacterium Prevotella copri DSM 18205T using glucose and xylose as carbon sources.Microbiologyopen. 2021 Jun;10(3):e1213. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1213. Microbiologyopen. 2021. PMID: 34180602 Free PMC article.
-
Medium development and production of carotenoids and exopolysaccharides by the extremophile Rhodothermus marinus DSM16675 in glucose-based defined media.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Oct 23;21(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01946-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36274123 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence of Antibiotic-Producing Bacillus velezensis H208, Isolated from Ginger Rhizosphere in Laifeng County, China.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023 Jan 24;12(1):e0055122. doi: 10.1128/mra.00551-22. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023. PMID: 36472451 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction provides insight into the metabolism of the thermophilic bacterium Rhodothermus marinus.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2025 Jan 7;101(1):fiae167. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiae167. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2025. PMID: 39716382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfredsson G, Kristjansson J, Hjörleifsdottir S, Stetter K. Rhodothermus marinus, gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic, halophilic bacterium from submarine hot springs in Iceland. J Gen Microbiol. 1988;134:299–306.
-
- Blücher A, Karlsson E, Holst O. Substrate-dependent production and some properties of a thermostable, α-galactosidase from Rhodothermus marinus. Biotechnol Lett. 2000;22:663–669. doi: 10.1023/A:1005627501609. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

