Glutathione as a mediator of cartilage oxidative stress resistance and resilience during aging and osteoarthritis
- PMID: 31522568
- PMCID: PMC6884680
- DOI: 10.1080/03008207.2019.1665035
Glutathione as a mediator of cartilage oxidative stress resistance and resilience during aging and osteoarthritis
Abstract
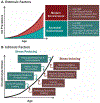
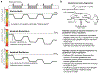
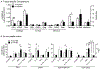
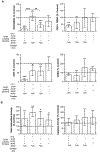
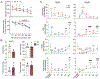
Purpose: An underlying cause of osteoarthritis (OA) is the inability of chondrocytes to maintain homeostasis in response to changing stress conditions. The purpose of this article was to review and experimentally evaluate oxidative stress resistance and resilience concepts in cartilage using glutathione redox homeostasis as an example. This framework may help identify novel approaches for promoting chondrocyte homeostasis during aging and obesity.Materials and Methods: Changes in glutathione content and redox ratio were evaluated in three models of chondrocyte stress: (1) age- and tissue-specific changes in joint tissues of 10 and 30-month old F344BN rats, including ex vivo patella culture experiments to evaluate N-acetylcysteine dependent resistance to interleukin-1beta; (2) effect of different durations and patterns of cyclic compressive loading in bovine cartilage on glutathione stress resistance and resilience pathways; (3) time-dependent changes in GSH:GSSG in primary chondrocytes from wild-type and Sirt3 deficient mice challenged with the pro-oxidant menadione.Results: Glutathione was more abundant in cartilage than meniscus or infrapatellar fat pad, although cartilage was also more susceptible to age-related glutathione oxidation. Glutathione redox homeostasis was sensitive to the duration of compressive loading such that load-induced oxidation required unloaded periods to recover and increase total antioxidant capacity. Exposure to a pro-oxidant stress enhanced stress resistance by increasing glutathione content and GSH:GSSG ratio, especially in Sirt3 deficient cells. However, the rate of recovery, a marker of resilience, was delayed without Sirt3.Conclusions: OA-related models of cartilage stress reveal multiple mechanisms by which glutathione provides oxidative stress resistance and resilience.
Keywords: Osteoarthritis; cartilage; glutathione; oxidative stress; resilience; stress resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
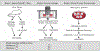
Similar articles
-
Effect of biomechanical stress on endogenous antioxidant networks in bovine articular cartilage.J Orthop Res. 2018 Feb;36(2):760-769. doi: 10.1002/jor.23728. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Orthop Res. 2018. PMID: 28892196 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of nitrotyrosine in aging and osteoarthritic cartilage: Correlation of oxidative damage with the presence of interleukin-1beta and with chondrocyte resistance to insulin-like growth factor 1.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Sep;46(9):2349-57. doi: 10.1002/art.10496. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 12355482
-
Increased oxidative stress with aging reduces chondrocyte survival: correlation with intracellular glutathione levels.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Dec;48(12):3419-30. doi: 10.1002/art.11338. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 14673993
-
Age-related degeneration of articular cartilage in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: molecular markers of senescent chondrocytes.Histol Histopathol. 2015 Jan;30(1):1-12. doi: 10.14670/HH-30.1. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Histol Histopathol. 2015. PMID: 25010513 Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species, aging and articular cartilage homeostasis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Feb 20;132:73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.038. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30176344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of biomarkers related to tryptophan metabolism in osteoarthritis.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Jun 30;39:101763. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101763. eCollection 2024 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39040542 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt3 Promotes Chondrogenesis, Chondrocyte Mitochondrial Respiration and the Development of High-Fat Diet-Induced Osteoarthritis in Mice.J Bone Miner Res. 2022 Dec;37(12):2531-2547. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4721. Epub 2022 Oct 27. J Bone Miner Res. 2022. PMID: 36214465 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the sirtuin family in cartilage and osteoarthritis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Dec 31;24(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02983-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36585687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role Played by Ferroptosis in Osteoarthritis: Evidence Based on Iron Dyshomeostasis and Lipid Peroxidation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 27;11(9):1668. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091668. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NADPH oxidase 4 deficiency attenuates experimental osteoarthritis in mice.RMD Open. 2023 Feb;9(1):e002856. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002856. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 36810185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kluzek S, Sanchez-Santos MT, Leyland KM, Judge A, Spector TD, Hart D, et al. Painful knee but not hand osteoarthritis is an independent predictor of mortality over 23 years follow-up of a population-based cohort of middle-aged women. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(10):1749–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
