Apatinib in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer after second-line or third-line chemotherapy: a phase II, single-arm, multicentre, prospective study
- PMID: 31523058
- PMCID: PMC6889407
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-019-0583-6
Apatinib in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer after second-line or third-line chemotherapy: a phase II, single-arm, multicentre, prospective study
Abstract
Background: Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains an aggressive cancer with short-term survival due to limited therapeutic options. Apatinib is a small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor that selectively inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of apatinib in patients with extensive-stage (EC) SCLC who had progressed after two or three previous therapies.
Methods: Eligible patients were histologically confirmed ES-SCLC after two or three previous treatments, including a platinum-based regimen. Patients received apatinib at an initial dose of 500 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was the objective response rate.
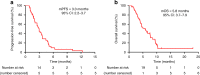
Results: Forty patients were enrolled. At the data cut-off time (November 15, 2018), the median follow-up was 7.4 months; no patients remained on treatment, and five were still in follow-up. An objective response was achieved in 7 of 40 patients (17.5%) in the intention-to-treat population, and 7 of 38 patients (18.4%) in the per-protocol population. The median progression-free survival and overall survival were 3.0 months and 5·8 months, respectively. The most commonly observed grade 3 or greater treatment-related adverse events were hypertension, hand-foot syndrome, increased L-gamma-glutamyltransferase.
Conclusions: Apatinib exhibited efficacy and an acceptable safety profile in previously heavily-treated ES-SCLC patients. Further exploration of apatinib in phase III trials is warranted.
Trial registration: NCT02945852.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Bishop K, Kosary CL, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2014, based on November 2016 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2017. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

