SWPepNovo: An Efficient De Novo Peptide Sequencing Tool for Large-scale MS/MS Spectra Analysis
- PMID: 31523183
- PMCID: PMC6743289
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.32142
SWPepNovo: An Efficient De Novo Peptide Sequencing Tool for Large-scale MS/MS Spectra Analysis
Abstract
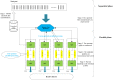
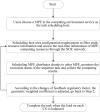
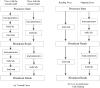
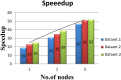
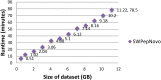
Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS)-based de novo peptide sequencing is a powerful method for high-throughput protein analysis. However, the explosively increasing size of MS/MS spectra dataset inevitably and exponentially raises the computational demand of existing de novo peptide sequencing methods, which is an issue urgently to be solved in computational biology. This paper introduces an efficient tool based on SW26010 many-core processor, namely SWPepNovo, to process the large-scale peptide MS/MS spectra using a parallel peptide spectrum matches (PSMs) algorithm. Our design employs a two-level parallelization mechanism: (1) the task-level parallelism between MPEs using MPI based on a data transformation method and a dynamic feedback task scheduling algorithm, (2) the thread-level parallelism across CPEs using asynchronous task transfer and multithreading. Moreover, three optimization strategies, including vectorization, double buffering and memory access optimizations, have been employed to overcome both the compute-bound and the memory-bound bottlenecks in the parallel PSMs algorithm. The results of experiments conducted on multiple spectra datasets demonstrate the performance of SWPepNovo against three state-of-the-art tools for peptide sequencing, including PepNovo+, PEAKS and DeepNovo-DIA. The SWPepNovo also shows high scalability in experiments on extremely large datasets sized up to 11.22 GB. The software and the parameter settings are available at https://github.com/ChuangLi99/SWPepNovo.
Keywords: Large-scale MS/MS spectra analysis; SW26010; de novo peptide sequencing; high performance computing.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures










References
-
- Gross J H. Tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrometry. Springer, Cham; 2017.
-
- Allmer J. Algorithms for the de novo sequencing of peptides from tandem mass spectra. Expert review of proteomics. 2011;8(5):645–657. - PubMed
-
- Eng J K, McCormack A L, Yates J R. An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. 1994;5(11):976–989. - PubMed
-
- Craig R, Beavis R C. TANDEM: matching proteins with tandem mass spectra. Bioinformatics. 2004;20(9):1466–1467. - PubMed
-
- Hirosawa M, Hoshida M, Ishikawa M. et al. MASCOT: multiple alignment system for protein sequences based on three-way dynamic programming. Bioinformatics. 1993;9(2):161–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

