Expression changes of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 proteins in the hippocampal CA1 field of the gerbil following transient global cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 31524247
- PMCID: PMC6658004
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4273
Expression changes of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 proteins in the hippocampal CA1 field of the gerbil following transient global cerebral ischemia
Abstract
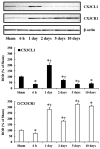
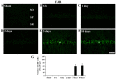
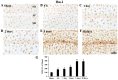
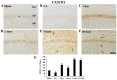
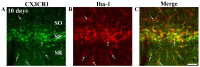
Chemokine C‑X3‑C motif ligand 1 (CX3CL1) and its sole receptor, CX3CR1, are known to be involved in neuronal damage/death following brain ischemia. In the present study, time‑dependent expression changes of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 proteins were investigated in the hippocampal CA1 field following 5 min of transient global cerebral ischemia (tgCI) in gerbils. To induce tgCI in gerbils, bilateral common carotid arteries were occluded for 5 min using aneurysm clips. Expression changes of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 proteins were assessed at 1, 2 and 5 days after tgCI using western blotting and immunohistochemistry. CX3CL1 immunoreactivity was strong in the CA1 pyramidal cells of animals in the sham operation group. Weak CX3CL1 immunoreactivity was detected at 6 h after tgCI, recovered at 1 day after tgCI and disappeared from 5 days after tgCI. CX3CR1 immunoreactivity was very weak in CA1 pyramidal cells of the sham animals. CX3CR1 immunoreactivity in CA1 pyramidal cells was significantly increased at 1 days after tgCI and gradually decreased thereafter. On the other hand, CX3CR1 immunoreactivity was significantly increased in microglia from 5 days after tgCI. These results showed that CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 protein expression levels in pyramidal cells and microglia in the hippocampal CA1 field following tgCI were changed, indicating that tgCI‑induced expression changes of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 proteins might be closely associated with tgCI‑induced delayed neuronal death and microglial activation.
Figures

References
-
- Lee JC, Kim IH, Park JH, Ahn JH, Cho JH, Cho GS, Tae HJ, Chen BH, Yan BC, Yoo KY, et al. Ischemic preconditioning protects hippocampal pyramidal neurons from transient ischemic injury via the attenuation of oxidative damage through upregulating heme oxygenase-1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;79:78–90. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.11.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park JH, Kim YH, Ahn JH, Choi SY, Hong S, Kim SK, Kang IJ, Kim YM, Lee TK, Won MH, Lee CH. Atomoxetine protects against NMDA receptor-mediated hippocampal neuronal death following transient global cerebral ischemia. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2017;14:158–168. doi: 10.2174/1567202614666170328094042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rastogi L, Godbole MM, Ray M, Rathore P, Rathore P, Pradhan S, Gupta SK, Pandey CM. Reduction in oxidative stress and cell death explains hypothyroidism induced neuroprotection subsequent to ischemia/reperfusion insult. Exp Neurol. 2006;200:290–300. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.02.013. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

