Design strategies for programmable oligonucleotide nanotherapeutics
- PMID: 31525462
- PMCID: PMC6980509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2019.09.006
Design strategies for programmable oligonucleotide nanotherapeutics
Abstract
A systematic review on how to design different programmable nanotherapeutics using oligonucleotides as building blocks or as surface and matrix modifiers for controlled and targeted delivery of various therapeutic agents in presented.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


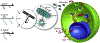


 = DNA,
= DNA,  = aptamer).
= aptamer).


References
-
- Gil ES et al. (2012) β-Cyclodextrin-poly(β-amino ester) nanoparticles for sustained drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier. Biomacromolecules 13, 3533–3541 - PubMed
-
- Gil ES et al. (2009) Quaternary ammonium beta-cyclodextrin nanoparticles for enhancing doxorubicin permeability across the in vitro blood–brain barrier. Biomacromolecules 10, 505–516 - PubMed
-
- Sahle FF et al. (2016) Formulation and in vitro evaluation of polymeric enteric nanoparticles as dermal carriers with pH-dependent targeting potential. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci 92, 98–109 - PubMed
-
- Sahle FF et al. (2017) Formulation and comparative in vitro evaluation of various dexamethasone-loaded pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticles intended for dermal applications. Int. J. Pharm 516, 21–31 - PubMed
-
- Müller RH et al. (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery – a review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm 50, 161–177 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

