ncRNA-Encoded Peptides or Proteins and Cancer
- PMID: 31526596
- PMCID: PMC6822234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.09.001
ncRNA-Encoded Peptides or Proteins and Cancer
Abstract
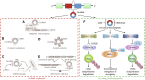
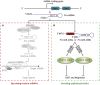
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are unique RNA transcripts that have been widely identified in the eukaryotic genome and have been shown to play key roles in the development of many cancers. However, the rapid development of genome-wide translation profiling and ribosome profiling has revealed that a small number of small open reading frames (sORFs) within ncRNAs actually have peptide- or protein-coding potential. The peptides or proteins encoded by ncRNA (HOXB-AS3, encoded by long ncRNA [lncRNA]; FBXW7-185aa, PINT-87aa, and SHPRH-146aa, encoded by circular RNA [circRNA]; and miPEP-200a and miPEP-200b, encoded by primary miRNAs) have been shown to be critical players in cancer development and progression, through effects upon the regulation of glucose metabolism, the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and the ubiquitination pathway. In this review, we summarize the reported peptides or proteins encoded by ncRNAs in cancer and explore the application of these peptides or proteins in the development of anti-tumor drugs and the identification of relevant therapeutic targets and tumor biomarkers.
Keywords: cancer; circRNA; lncRNA; miRNA; ncRNA; peptide; protein.
Copyright © 2019 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

