miR-125a-5p inhibits tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31527306
- PMCID: PMC6781988
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.102276
miR-125a-5p inhibits tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
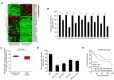
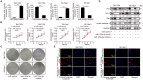
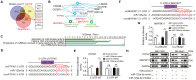
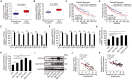
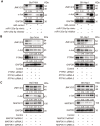
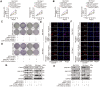
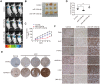
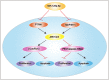
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most prevalent and deadly cancers world-wide. miR-125a-5p is a tumor suppressor in HCC and other cancers, but its mechanisms of action during HCC tumorigenesis remain largely unknown. In this study, we found that miR-125a-5p expression was significantly lower in HCC tissues and cell lines than matched normal tissues and liver cells. miR-125a-5p overexpression inhibited HCC cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo, while miR-125a-5p knockdown had the opposite effects. In addition, PTPN1 and MAP3K11 were identified as targets of miR-125a-5p. Knocking down PTPN1 and MAP3K11 activated the JNK MAPK signaling pathway to suppress HCC cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. Our findings suggest that miR-125a-5p may be a useful therapeutic target for treatment of HCC patients.
Keywords: HCC; MAP3K11; MAPK signaling pathway; PTPN1; miR-125a-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-548a-5p promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting Tg737.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 21;22(23):5364-73. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5364. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27340352 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-98-5p Inhibits Tumorigenesis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting NF-κB-Inducing Kinase.Yonsei Med J. 2020 Jun;61(6):460-470. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.6.460. Yonsei Med J. 2020. PMID: 32469170 Free PMC article.
-
Astemizole promotes the anti-tumor effect of vitamin D through inhibiting miR-125a-5p-meidated regulation of VDR in HCC.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:1682-1691. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.153. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30257386
-
miRNAs affect the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via dysregulation of their biogenesis and expression.Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Jul 11;12:45. doi: 10.1186/s12964-014-0045-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 25012758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dichotomous role of TGF-β in controlling liver cancer cell survival and proliferation.J Genet Genomics. 2020 Sep 20;47(9):497-512. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Nov 14. J Genet Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33339765 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNA Related to MAPK Signaling Pathway in Liver Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 7;23(19):11908. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911908. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small extravesicular microRNA in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its potential as a liquid biopsy for early detection.Head Neck. 2023 Jan;45(1):212-224. doi: 10.1002/hed.27231. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Head Neck. 2023. PMID: 36271833 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway.Open Life Sci. 2022 Sep 19;17(1):1229-1239. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0498. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36213383 Free PMC article.
-
HPV-Related Cervical Cancer and Extracellular Vesicles.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Oct 25;12(11):2584. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112584. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals PTPN1 (PTP1B) Is a Promising Immunotherapy Target Associated with T Cell Function for Liver Cancer.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jan 27;2023:1533794. doi: 10.1155/2023/1533794. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 36741874 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

