Clinical experience with management of Hoffa fractures using headless compression screw and headed screw
- PMID: 31528071
- PMCID: PMC6739431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.10.011
Clinical experience with management of Hoffa fractures using headless compression screw and headed screw
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing declaration of competing interest statements in previously published articles.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 Nov-Dec;11(6):1176. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.10.024. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 33192027 Free PMC article.
Abstract
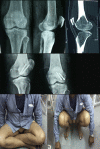
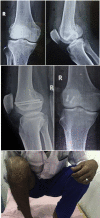
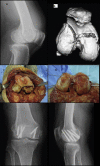
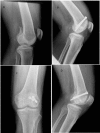
Purpose: to analyze the radiological and functional outcomes of patients after surgical treatment of coronal plane fractures of femoral condyle using headless compression screw and cannulated cancellous (CC) screws (headed screws).
Material and method: In this prospective study 30 cases were included, out of which 15 were treated with headed screws and other 15 were treated with headless screws. Active knee mobilization exercises were started from the third postoperative day. Initially, patients were kept non-weight bearing; partial weight bearing was started at 10 weeks and progressed to full weight bearing as tolerated. Follow-up visits conducted at 2, 4 and 12 weeks, thereafter at 6 and 12 months. The long term final results were rated using Neer's rating system.
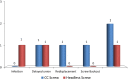
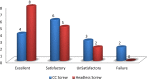
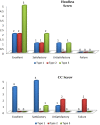
Results: Results were graded as excellent (score > 85), Satisfactory (score 71-85), Unsatisfactory (score 56-70), and Failure (score < 55). In CC screw group the outcome was good in 10 cases (66.66%) and poor in 5 cases (33.33%) whereas in headless group outcome was good in 13 cases (86.66%) and poor in 2 (13.33%).
Conclusion: fixation of Hoffa fracture with headless compression screw in comparison to CC screw (Headed Screw) have no significant difference in terms of functional outcome like range of motion but complications and implant failure is significantly higher in cases fixed with CC screw than in headless screw. So we conclude that overall outcome is better in study group fixed with headless compression screw as compared to cases fixed with CC Screw.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffa A. fourth ed. Ferdinand Enke-Verlag; Stuttgart: 1904. Lehrbuch der Frakturen und Luxationen.
-
- Manfredini M., Gildone A., Ferrante R., Bernasconi S., Massari L. Unicondylar femoral fractures : therapeutic strategy and long term results. A review of 23 patients. Acta Orthop Belg. 2001;67(2):132–138. - PubMed
-
- Letenneur J., Labour P.R., Rogez J.M., Lignon J., Bainvel J.V. Fractures de Hoffa: a propos de observations. Ann Chir. 1978;32 213—9 (Eng. Absr.) - PubMed
-
- Nork S.E., Segina D.N., Aflatoon K. The association between supracondylar- intercondylar distal femoral fractures and coronal plane fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(3):564–569. - PubMed
-
- Butler M.S., Brumback R.J., Ellison T.S., Poka A., Bathon G.H., Burgess A.R. Interlocking intramedullary nailing for ipsilateral fractures of the femoral shaft and distal part of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73:1492–1502. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

