Incidence and mechanism of injury of clavicle fractures in the NEISS database: Athletic and non athletic injuries
- PMID: 31528074
- PMCID: PMC6738494
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2019.01.019
Incidence and mechanism of injury of clavicle fractures in the NEISS database: Athletic and non athletic injuries
Abstract
Background: Clavicle fractures are a very common injury due to accidental trauma, specifically during athletics. The purpose of this study was (1) to determine the incidence of clavicle fractures presenting to United States emergency departments; (2) to compare the rate of clavicle injuries from 2012 to 2015 to 2002-2005 (3) to determine the most common mechanisms of injury for clavicle fractures.
Methods: The National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS) was queried for the years 2002-2005 and 2012-2015. Examined variables included patient age, sex, and year of admission. Total annual case numbers were estimated using NEISS hospital weights. Annual injury incidence rates by age group and patient sex were calculated based on yearly U.S. Census estimates. Chi square test and logistic regression were used to compare injury rates by sex and age groups. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
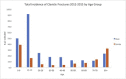
Results: During the 8 years studied, the participating emergency departments (EDs) coded 14,795 fracture exposures. Using weighted estimates, this represent 545,663 injuries nationally (95% CL 425,986-665,339). This resulted in an incidence of 22.4 injuries per 100,000 person years (95% CL 17.5-27.3). The most common causes of injury were bicycles (15.1%), football (10.7%), beds/bedframes (6.8%), stairs (5.4%), and floors (4.0%). Fifty percent of clavicle fractures were due to an athletic activity. There was no significant change in injuries from 2002 to 2005 compared to 2012-2015 (23.1 per 100,000, 95% CL 18.5-27.7, and 22.4 per 100,000 person years (95% CL 17.5-27.3), respectively).
Conclusion: Clavicle fractures continue to occur at similar rates, with athletics accounting for 50% of injuries. Patients most at risk for clavicle fracture was bimodal in nature, with males aged 0-19 being the most common. Females were most at risk between 0 and 9 years old. We found that clavicle fracture continued to occur at similar rates as compared to 10 years prior, especially in active populations participating in collision sports (bicycle, football, and soccer).
Keywords: Clavicle fracture; Collision sports; Emergency department; Epidemiology; Sports.
Figures
References
-
- Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Carry P.M., Koonce R., Pan Z., Polousky J.D. A survey of physician opinion: adolescent midshaft clavicle fracture treatment preferences among POSNA members. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(1):44–49. - PubMed
-
- Vander Have K.L., Perdue A.M., Caird M.S., Farley F a. Operative versus nonoperative treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures in adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30(4):307–312. - PubMed
-
- Hill J.M., McGuire M.H., Crosby L.A. Closed treatment of displaced middle-third fractures of the clavicle gives poor results. J Bone Jt Surg. 1997;79(4):537–539. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources