Eosinophilic esophagitis: Current concepts in diagnosis and treatment
- PMID: 31528089
- PMCID: PMC6718043
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4598
Eosinophilic esophagitis: Current concepts in diagnosis and treatment
Abstract
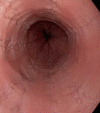
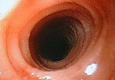
Eosinophilic esophagitis is an immune-allergic pathology of multifactorial etiology (genetic and environmental) that affects both pediatric and adult patients. Its symptoms, which include heartburn, regurgitation, and esophageal stenosis (with dysphagia being more frequent in eosinophilic esophagitis in young adults and children), are similar to those of gastroesophageal reflux disease, causing delays in diagnosis and treatment. Although endoscopic findings such as furrows, esophageal mucosa trachealization, and whitish exudates may suggest its presence, this diagnosis should be confirmed histologically based on the presence of more than 15 eosinophils per high-power field and the exclusion of other causes of eosinophilia (parasitic infections, hypereosinophilic syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, among others) for which treatment could be initiated. Currently, the 3 "D"s ("Drugs, Diet, and Dilation") are considered the fundamental components of treatment. The first 2 components, which involve the use of proton pump inhibitors, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants and empirical diets or guided food elimination based on allergy tests, are more useful in the initial phases, whereas endoscopic dilation is reserved for esophageal strictures. Herein, the most important aspects of eosinophilic esophagitis pathophysiology will be reviewed, in addition to evidence for the various treatments.
Keywords: Corticoid; Diet; Dilation; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Esophageal stenosis; Proton pump inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Landres RT, Kuster GG, Strum WB. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology. 1978;74:1298–1301. - PubMed
-
- Attwood SE, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, Jones JB. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:109–116. - PubMed
-
- Straumann A, Spichtin HP, Bernoulli R, Loosli J, Vögtlin J. [Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis: a frequently overlooked disease with typical clinical aspects and discrete endoscopic findings] Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1994;124:1419–1429. - PubMed
-
- Navarro P, Arias Á, Arias-González L, Laserna-Mendieta EJ, Ruiz-Ponce M, Lucendo AJ. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the growing incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49:1116–1125. - PubMed
-
- Kapel RC, Miller JK, Torres C, Aksoy S, Lash R, Katzka DA. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a prevalent disease in the United States that affects all age groups. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1316–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

