Exploring the hepatitis C virus genome using single molecule real-time sequencing
- PMID: 31528092
- PMCID: PMC6718035
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4661
Exploring the hepatitis C virus genome using single molecule real-time sequencing
Abstract
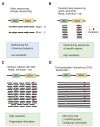
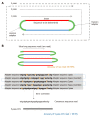
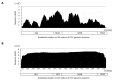
Single molecular real-time (SMRT) sequencing, also called third-generation sequencing, is a novel sequencing technique capable of generating extremely long contiguous sequence reads. While conventional short-read sequencing cannot evaluate the linkage of nucleotide substitutions distant from one another, SMRT sequencing can directly demonstrate linkage of nucleotide changes over a span of more than 20 kbp, and thus can be applied to directly examine the haplotypes of viruses or bacteria whose genome structures are changing in real time. In addition, an error correction method (circular consensus sequencing) has been established and repeated sequencing of a single-molecule DNA template can result in extremely high accuracy. The advantages of long read sequencing enable accurate determination of the haplotypes of individual viral clones. SMRT sequencing has been applied in various studies of viral genomes including determination of the full-length contiguous genome sequence of hepatitis C virus (HCV), targeted deep sequencing of the HCV NS5A gene, and assessment of heterogeneity among viral populations. Recently, the emergence of multi-drug resistant HCV viruses has become a significant clinical issue and has been also demonstrated using SMRT sequencing. In this review, we introduce the novel third-generation PacBio RSII/Sequel systems, compare them with conventional next-generation sequencers, and summarize previous studies in which SMRT sequencing technology has been applied for HCV genome analysis. We also refer to another long-read sequencing platform, nanopore sequencing technology, and discuss the advantages, limitations and future perspectives in using these third-generation sequencers for HCV genome analysis.
Keywords: Hepatitis C virus; Nanopore sequencer; PacBio RSII; Resistance-associated substitution; Single molecule real-time sequencing; Third generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest. No financial support was received for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Chayama K, Takahashi S, Toyota J, Karino Y, Ikeda K, Ishikawa H, Watanabe H, McPhee F, Hughes E, Kumada H. Dual therapy with the nonstructural protein 5A inhibitor, daclatasvir, and the nonstructural protein 3 protease inhibitor, asunaprevir, in hepatitis C virus genotype 1b-infected null responders. Hepatology. 2012;55:742–748. - PubMed
-
- Kumada H, Chayama K, Rodrigues L, Jr, Suzuki F, Ikeda K, Toyoda H, Sato K, Karino Y, Matsuzaki Y, Kioka K, Setze C, Pilot-Matias T, Patwardhan M, Vilchez RA, Burroughs M, Redman R. Randomized phase 3 trial of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir for hepatitis C virus genotype 1b-infected Japanese patients with or without cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2015;62:1037–1046. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumada H, Suzuki Y, Ikeda K, Toyota J, Karino Y, Chayama K, Kawakami Y, Ido A, Yamamoto K, Takaguchi K, Izumi N, Koike K, Takehara T, Kawada N, Sata M, Miyagoshi H, Eley T, McPhee F, Damokosh A, Ishikawa H, Hughes E. Daclatasvir plus asunaprevir for chronic HCV genotype 1b infection. Hepatology. 2014;59:2083–2091. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayashi N, Izumi N, Kumada H, Okanoue T, Tsubouchi H, Yatsuhashi H, Kato M, Ki R, Komada Y, Seto C, Goto S. Simeprevir with peginterferon/ribavirin for treatment-naïve hepatitis C genotype 1 patients in Japan: CONCERTO-1, a phase III trial. J Hepatol. 2014;61:219–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

