Cellular Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment: The Role of Secretome
- PMID: 31528221
- PMCID: PMC6746126
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.21780
Cellular Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment: The Role of Secretome
Abstract
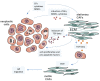
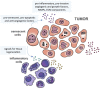
Over the past years, it has become evident that cancer initiation and progression depends on several components of the tumor microenvironment, including inflammatory and immune cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, adipocytes, and extracellular matrix. These components of the tumor microenvironment and the neoplastic cells interact with each other providing pro and antitumor signals. The tumor-stroma communication occurs directly between cells or via a variety of molecules secreted, such as growth factors, cytokines, chemokines and microRNAs. This secretome, which derives not only from tumor cells but also from cancer-associated stromal cells, is an important source of key regulators of the tumorigenic process. Their screening and characterization could provide useful biomarkers to improve cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of treatment responses.
Keywords: Cancer; Microenvironment; Secretome..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Paltridge JL, Belle L, Khew-Goodall Y. The secretome in cancer progression. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2013;1834:2233–41. - PubMed
-
- Schaaij-Visser TB, de Wit M, Lam SW, Jimenez CR. The cancer secretome, current status and opportunities in the lung, breast and colorectal cancer context. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2013;1834:2242–58. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal GK, Jwa NS, Lebrun MH, Job D, Rakwal R. Plant secretome: unlocking secrets of the secreted proteins. Proteomics. 2010;10:799–827. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

