Perceptual awareness and active inference
- PMID: 31528360
- PMCID: PMC6734140
- DOI: 10.1093/nc/niz012
Perceptual awareness and active inference
Abstract
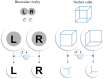
Perceptual awareness depends upon the way in which we engage with our sensorium. This notion is central to active inference, a theoretical framework that treats perception and action as inferential processes. This variational perspective on cognition formalizes the notion of perception as hypothesis testing and treats actions as experiments that are designed (in part) to gather evidence for or against alternative hypotheses. The common treatment of perception and action affords a useful interpretation of certain perceptual phenomena whose active component is often not acknowledged. In this article, we start by considering Troxler fading - the dissipation of a peripheral percept during maintenance of fixation, and its recovery during free (saccadic) exploration. This offers an important example of the failure to maintain a percept without actively interrogating a visual scene. We argue that this may be understood in terms of the accumulation of uncertainty about a hypothesized stimulus when free exploration is disrupted by experimental instructions or pathology. Once we take this view, we can generalize the idea of using bodily (oculomotor) action to resolve uncertainty to include the use of mental (attentional) actions for the same purpose. This affords a useful way to think about binocular rivalry paradigms, in which perceptual changes need not be associated with an overt movement.
Keywords: Bayesian; Troxler fading; active inference; awareness; binocular rivalry.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Reinforcement of perceptual inference: reward and punishment alter conscious visual perception during binocular rivalry.Front Psychol. 2014 Dec 3;5:1377. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01377. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 25520687 Free PMC article.
-
Scene Construction, Visual Foraging, and Active Inference.Front Comput Neurosci. 2016 Jun 14;10:56. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2016.00056. eCollection 2016. Front Comput Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27378899 Free PMC article.
-
Can binocular rivalry reveal neural correlates of consciousness?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Mar 17;369(1641):20130211. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0211. Print 2014 May 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24639582 Free PMC article.
-
Time course of visual perception: coarse-to-fine processing and beyond.Prog Neurobiol. 2008 Apr;84(4):405-39. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2007.09.001. Epub 2007 Sep 29. Prog Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 17976895 Review.
-
Predictive coding explains binocular rivalry: an epistemological review.Cognition. 2008 Sep;108(3):687-701. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2008.05.010. Epub 2008 Jul 22. Cognition. 2008. PMID: 18649876 Review.
Cited by
-
Context-Sensitive Conscious Interpretation and Layer-5 Pyramidal Neurons in Multistable Perception.Brain Behav. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70393. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70393. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40038853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated world modeling theory expanded: Implications for the future of consciousness.Front Comput Neurosci. 2022 Nov 24;16:642397. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2022.642397. eCollection 2022. Front Comput Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36507308 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience phenotypes derived from an active inference account of allostasis.Front Behav Neurosci. 2025 May 9;19:1524722. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2025.1524722. eCollection 2025. Front Behav Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40416792 Free PMC article.
-
Generative Models for Active Vision.Front Neurorobot. 2021 Apr 13;15:651432. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2021.651432. eCollection 2021. Front Neurorobot. 2021. PMID: 33927605 Free PMC article.
-
Bistable perception, precision and neuromodulation.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Jan 14;34(1):bhad401. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhad401. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 37950879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alais D, van Boxtel JJ, Parker A. et al. Attending to auditory signals slows visual alternations in binocular rivalry. Vision Res 2010;50:929–35. - PubMed
-
- Alpers GW, Gerdes ABM.. Here is looking at you: emotional faces predominate in binocular rivalry. Emotion 2007;7:495–506. - PubMed
-
- Bachy R, Zaidi Q.. Factors governing the speed of color adaptation in foveal versus peripheral vision. J Opt Soc Am A 2014;31:A220–5. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman RL, Milders M, De Gelder B. et al. Influence of emotional facial expressions on binocular rivalry. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2008;28:317–26. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
