Effect of Behavioral and Pelvic Floor Muscle Therapy Combined With Surgery vs Surgery Alone on Incontinence Symptoms Among Women With Mixed Urinary Incontinence: The ESTEEM Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 31529007
- PMCID: PMC6749544
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2019.12467
Effect of Behavioral and Pelvic Floor Muscle Therapy Combined With Surgery vs Surgery Alone on Incontinence Symptoms Among Women With Mixed Urinary Incontinence: The ESTEEM Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Mixed urinary incontinence, including both stress and urgency incontinence, has adverse effects on a woman's quality of life. Studies evaluating treatments to simultaneously improve both components are lacking.
Objective: To determine whether combining behavioral and pelvic floor muscle therapy with midurethral sling is more effective than sling alone for improving mixed urinary incontinence symptoms.
Design, setting, and participants: Randomized clinical trial involving women 21 years or older with moderate or severe stress and urgency urinary incontinence symptoms for at least 3 months, and at least 1 stress and 1 urgency incontinence episode on a 3-day bladder diary. The trial was conducted across 9 sites in the United States, enrollment between October 2013 and April 2016; final follow-up October 2017.
Interventions: Behavioral and pelvic floor muscle therapy (included 1 preoperative and 5 postoperative sessions through 6 months) combined with midurethral sling (n = 209) vs sling alone (n = 207).
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was change between baseline and 12 months in mixed incontinence symptoms measured by the Urogenital Distress Inventory (UDI) long form; range, 0 to 300 points; minimal clinically important difference, 35 points, with higher scores indicating worse symptoms.
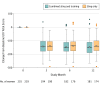
Results: Among 480 women randomized (mean [SD] age, 54.0 years [10.7]), 464 were eligible and 416 (86.7%) had postbaseline outcome data and were included in primary analyses. The UDI score in the combined group significantly decreased from 178.0 points at baseline to 30.7 points at 12 months, adjusted mean change -128.1 points (95% CI, -146.5 to -109.8). The UDI score in the sling-only group significantly decreased from 176.8 to 34.5 points, adjusted mean change -114.7 points (95% CI, -133.3 to -96.2). The model-estimated between-group difference (-13.4 points; 95% CI, -25.9 to -1.0; P = .04) did not meet the minimal clinically important difference threshold. Related and unrelated serious adverse events occurred in 10.2% of the participants (8.7% combined and 11.8% sling only).
Conclusions and relevance: Among women with mixed urinary incontinence, behavioral and pelvic floor muscle therapy combined with midurethral sling surgery compared with surgery alone resulted in a small statistically significant difference in urinary incontinence symptoms at 12 months that did not meet the prespecified threshold for clinical importance.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01959347.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Evidence-Based Treatment for Mixed Urinary Incontinence.JAMA. 2019 Sep 17;322(11):1049-1051. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.12659. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31528991 No abstract available.
-
Re: Effect of Behavioral and Pelvic Floor Muscle Therapy Combined with Surgery vs Surgery Alone on Incontinence Symptoms among Women with Mixed Urinary Incontinence: The ESTEEM Randomized Clinical Trial.J Urol. 2020 Apr;203(4):670-671. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000733.03. Epub 2020 Jan 13. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31928487 No abstract available.
-
Measuring Clinical Importance in a Trial of Interventions for Mixed Urinary Incontinence.JAMA. 2020 Feb 4;323(5):479. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.19730. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32016303 No abstract available.
-
Editorial Comment: Effect of Behavioral and Pelvic Floor Muscle Therapy Combined With Surgery vs Surgery Alone on Incontinence Symptoms Among Women With Mixed Urinary Incontinence: The ESTEEM Randomi-zed Clinical Trial.Int Braz J Urol. 2020 Jul-Aug;46(4):669-670. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.04.12. Int Braz J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32374137 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HD054215/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069025/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD069013/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069010/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD054214/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD069031/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD069006/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069006/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD069010/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD069013/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD041261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD069031/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

