In-Hospital Physiotherapy and Physical Recovery 3 Months After Lung Cancer Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31530046
- PMCID: PMC6751530
- DOI: 10.1177/1534735419876346
In-Hospital Physiotherapy and Physical Recovery 3 Months After Lung Cancer Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
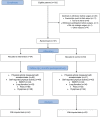
Background. Lung cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and one of the leading causes of cancer deaths. Surgery is the primary approach for curative treatment. Postoperative complications are common, and physiotherapy is often routinely provided for their prevention and treatment, even though the evidence is limited. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of in-hospital physiotherapy on postoperative physical capacity, physical activity, and lung function among patients undergoing lung cancer surgery. Methods. A total of 107 patients undergoing elective thoracic surgery were included in a single-blinded randomized controlled trial, and randomized to a study group, receiving in-hospital physiotherapy treatment, or a control group, not receiving in-hospital physiotherapy treatment. The patients were assessed preoperatively and 3 months after surgery. The in-hospital physiotherapy treatment consisted of early mobilization, ambulation, breathing exercises, and thoracic range of motion exercises. Physical capacity was assessed with the 6-minute walk test. Level of physical activity was objectively assessed with an accelerometer and subjectively assessed with the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Modified for the Elderly. Results. Physical capacity for the whole sample was significantly decreased 3 months postoperatively compared with preoperative values (P = .047). There were no statistically significant differences between the groups regarding physical capacity, physical activity, spirometric values, or dyspnea. However, patients in the study group increased their level of self-reported physical activity from preoperatively to 3 months postoperatively, while the patients in the control group did not. Conclusions. No difference in physical capacity, physical activity, or lung function was found 3 months postoperatively in lung cancer surgery patients receiving in-hospital physiotherapy compared with control patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01961700.
Keywords: lung cancer; physical activity; physical function; physiotherapy; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87-108. - PubMed
-
- Howington JA, Blum MG, Chang AC, Balekian AA, Murthy SC. Treatment of stage I and II non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 suppl):e278S-313S. - PubMed
-
- Wildgaard K, Ravn J, Nikolajsen L, Jakobsen E, Jensen TS, Kehlet H. Consequences of persistent pain after lung cancer surgery: a nationwide questionnaire study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55:60-68. - PubMed