Personalized 18FDG Dose Synthesis Using BG-75 Generator: 1st Year Experience at JCI Accredited Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan
- PMID: 31531293
- PMCID: PMC6709360
- DOI: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.792
Personalized 18FDG Dose Synthesis Using BG-75 Generator: 1st Year Experience at JCI Accredited Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan
Abstract
Background: Compact cyclotrons are getting popular to fulfill enormous current demands of PET tracers. Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan has acquired the first smallest footprint of BG-75 Generator for 18FDG-based PET/CT clinical imaging. We are sharing our experience of BG-75 in the first year (December 2015-November 2016) after commissioning.
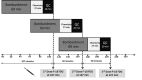
Material and methods: BG-75 Generator (ABT, USA) was installed in available space without major design modification. It has a self-shielded mini-cyclotron (7.5 MeV proton beam, positive ion with current < 5µA) to produce [18F]F-, an automated card-based radiochemistry module to produce 18FDG and automated QC module to perform tests upon each batch of 18FDG. Data were collected for yields of [18F]F-, 18FDG, QC and radiation safety parameters.
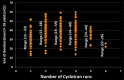
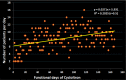
Results: Total 545 runs in 167 days (3±01 runs/day) were made. Average yield with 60 minute bombardment using 4.5 µA current was 37 mCi and 21 mCi for [18F]F- and 18FDG, respectively. Total 29 runs had chemistry or QC failures and were discarded. Remaining 516 batches were used to perform imaging upon 1370 patients (8±03 patients/day). Radiation dose in BG-75 suite and effective doses to 02 operators were within statutory limits.
Conclusion: BG-75 Generator provides safe, dependable and sustainable supply of 18F-Fluoride for 18FDG and other low-volume clinical PET imaging. Its compactness and automation need minimal space and manpower. Radiation dose rate in cyclotron suite and personal dosimetry were also found within safe limits. Its Dose-on-Demand workflow offers a new concept of Personalized Dose Preparation which is currently not possible with a conventional cyclotron.
Keywords: Fluorodeoxyglucose 18F; Cyclotron; Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography.
Figures
References
-
- Avril N E, Weber W A. Monitoring response to treatment in patients utilizing PET. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005;43:189–204. - PubMed
-
- Uz Zaman M, Fatima N, Sajjad Z, Zaman U, Tahseen R, Zaman A. 18FDG synthesis and supply: a journey from existing centralized to future decentralized models. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:10057–9. - PubMed
-
- Hamacher K, Coenen H H, Stöcklin G. Efficient stereospecific synthesis of no-carrier-added 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution. Journal of nuclear medicine: official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 1986;27:235–8. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, U.S. Pharmacopeia 36th ed., The National Formulary 31st ed., General Chapter 714 Sterility Tests, 2013 .
-
- Boellaard R, Delgado-Bolton R, Oyen W J, Giammarile F, Tatsch K, Eschner W, et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: version 2.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:328–54. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2961-x. [ PMC Free Article] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
