Solver Device for Powdery Drugs
- PMID: 31531305
- PMCID: PMC6709353
- DOI: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.795
Solver Device for Powdery Drugs
Abstract
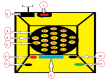
Pharmacotherapy is a major treatment method in healthcare centers, and the injection of powdered drugs is among common pharmacotherapy techniques. Medication errors and nosocomial infections are among major health issues in the world. On the other hand, powdered drugs are widely used in hospitals; however, drug mixture is a very time-consuming process. The objective of this invention was to accelerate drug vial mixture, reduce medication errors and nosocomial infections, and save time. There are different drug mixing devices, each with specific abilities. The present invention not only possesses the abilities of other devices but also can mix drugs [with a diluent] with higher quality and accuracy. The drug vial mixing device can mix 20 vials at adjustable time and speed with high quality and accuracy. This device is equipped with an infrared system to ensure a complete mixture of powder, and a Bluetooth short range radio system to remotely control all monitoring options of the device. This is a small and simple-to-use device. The drug vial mixing device can effectively reduce medication errors and nosocomial infections, and save time.
Keywords: Cross Infection; Drug Compounding; Medical Errors; Powders.
Figures
References
-
- Gahart B, Nazareno A. Intravenous medications, 27th edition. Elsevier: 2011.
-
- Trissel L A. Handbook on injectable drugs. 2003.
-
- Mewshaw M R, White K M, Walrath J. Medical errors: where are we now? Nurs Manage. 2006;37:50–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
