Clinical outcomes and safety of high-resolution manometry guided superficial partial circular muscle myotomy in per-oral endoscopic myotomy for Jackhammer esophagus: Two cases report
- PMID: 31531326
- PMCID: PMC6718798
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2322
Clinical outcomes and safety of high-resolution manometry guided superficial partial circular muscle myotomy in per-oral endoscopic myotomy for Jackhammer esophagus: Two cases report
Abstract
Background: Jack hammer esophagus is a relatively rare disease and to date, there is no dramatic treatment option. Recently, conventional per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) have expanded their area into Jackhammer esophagus. However, several complications such as post procedure motility disorders (e.g., passage disturbance) are issues after POEM. To overcome these issues, we here introduced high-resolution manometry (HRM)-guided superficial partial circular muscle myotomy, which involves cutting only the superficial layer of the esophageal circular muscle.
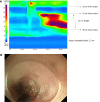
Case summary: We report two cases of patients with Jackhammer esophagus who were treated with HRM-guided extremely superficial partial circular muscle myotomy during POEM. Case 1 was a 53-year-old female with medication-refractory odynophagia and case 2 was a 47-year-old man who presented with chest pain. They were diagnosed with Jackhammer esophagus using HRM, and the hypercontractile segments of the esophagus were identified. HRM-guided extremely superficial partial circular muscle myotomy was performed while preserving the lower esophageal sphincter. Therefore, the circular and longitudinal muscle layers are preserved but hypercontractile movements are reduced, even after POEM. Patients' clinical symptoms dramatically improved right after POEM, and 6-mo follow-up HRM revealed completely resolved status. During a 1-year follow-up period, patients were still in good health and remained symptom free.
Conclusion: HRM-guided superficial partial circular muscle myotomy may be a promising alternative to conventional POEM for treating Jackhammer esophagus with improved efficacy.
Keywords: Case report; Hypercontractile; Jackhammer esophagus; Partial circular muscle myotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kandulski A, Fuchs KH, Weigt J, Malfertheiner P. Jackhammer esophagus: high-resolution manometry and therapeutic approach using peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) Dis Esophagus. 2016;29:695–696. - PubMed
-
- Herregods TV, Smout AJ, Ooi JL, Sifrim D, Bredenoord AJ. Jackhammer esophagus: Observations on a European cohort. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017:29. - PubMed
-
- Jia Y, Arenas J, Hejazi RA, Elhanafi S, Saadi M, McCallum RW. Frequency of Jackhammer Esophagus as the Extreme Phenotypes of Esophageal Hypercontractility Based on the New Chicago Classification. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50:615–618. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

