Hydroxychloroquine Blood Levels Predict Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy
- PMID: 31532077
- PMCID: PMC7050401
- DOI: 10.1002/art.41121
Hydroxychloroquine Blood Levels Predict Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy
Abstract
Objective: In 2016, the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) changed the recommended daily dose of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) from 6.5 mg/kg to <5 mg/kg. However, it is not clear that the lower prescribed dose of HCQ will have the same efficacy for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) activity or the same role in protecting against cardiovascular risk factors and thrombosis. This study was undertaken to address the frequency of HCQ retinopathy and the role of HCQ blood levels in identifying those individuals who are at a greater future risk of retinopathy.
Methods: HCQ blood levels in 537 patients with SLE from a large clinical cohort were repeatedly measured, and patients were tested for HCQ retinopathy. We assessed the risk of retinopathy according to clinical characteristics and blood levels of HCQ.
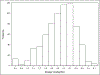
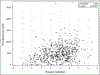
Results: The overall frequency of retinopathy was 4.3% (23 of 537 patients). There was a 1% risk of retinopathy in the first 5 years of HCQ treatment, 1.8% from 6 to 10 years, 3.3% from 11 to 15 years, 11.5% from 16 to 20 years, and 8.0% after 21 years of use. We found that older age (P < 0.0001), higher body mass index (P for trend = 0.0160), and longer duration of HCQ intake (P = 0.0024 and P for trend = 0.0006) were associated with a higher risk of HCQ toxicity. Higher blood levels of HCQ predicted later HCQ retinopathy (P = 0.0124 and P = 0.0340 for mean and maximum HCQ blood levels, respectively).
Conclusion: Our data prove the utility of assessing blood levels of HCQ in the prediction of retinopathy. This would allow clinicians to either decrease the dose or increase monitoring in those patients with high HCQ blood levels.
© 2019, American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Reply.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr;72(4):694. doi: 10.1002/art.41146. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31631561 No abstract available.
-
Additional Analyses to Confirm Relationship of Hydroxychloroquine Blood Levels to Retinopathy: Comment on the Article by Petri et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr;72(4):694. doi: 10.1002/art.41148. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31631577 No abstract available.
-
Do Hydroxychloroquine Blood Levels and Dose Identify Different Populations at Risk of Retinopathy? Comment on the Article by Petri et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Dec;72(12):2165-2166. doi: 10.1002/art.41464. Epub 2020 Oct 11. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32741122 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Dec;72(12):2166. doi: 10.1002/art.41462. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32741151 No abstract available.
-
Early-Onset Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy and a Possible Relationship to Blood Levels: Comment on the Article by Petri et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Feb;73(2):358-359. doi: 10.1002/art.41497. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32856370 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Feb;73(2):359. doi: 10.1002/art.41521. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32936524 No abstract available.
-
Different Control Populations May Lead to Different Understanding of Hydroxychloroquine Blood Levels as a Risk Factor for Retinopathy: Comment on the Article by Petri et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Apr;73(4):715. doi: 10.1002/art.41588. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33191634 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ruiz-Irastorza G, Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zeron P, Khamashta MA. Clinical efficacy and side effects of antimalarials in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:20–28. - PubMed
-
- Fessler BJ, Alarcón GS, McGwin G, Roseman J, Bastian HM, Friedman AW, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups: XVI. Association of hydroxychloroquine use with reduced risk of damage accrual. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:1473–1480. - PubMed
-
- Sutton EJ, Davidson JE, Bruce IN. The Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) damage index: A systematic literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2013;43:352–361. - PubMed
-
- The Canadian Hydroxychloroquine Study Group. A randomized study of the effect of withdrawing hydroxychloroquine sulfate in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 1991;324:150–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical