Genome wide genetic dissection of wheat quality and yield related traits and their relationship with grain shape and size traits in an elite × non-adapted bread wheat cross
- PMID: 31532783
- PMCID: PMC6750600
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221826
Genome wide genetic dissection of wheat quality and yield related traits and their relationship with grain shape and size traits in an elite × non-adapted bread wheat cross
Abstract
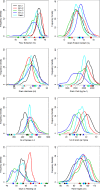
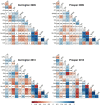
The genetic gain in yield and quality are two major targets of wheat breeding programs around the world. In this study, a high density genetic map consisting of 10,172 SNP markers identified a total of 43 genomic regions associated with three quality traits, three yield traits and two agronomic traits in hard red spring wheat (HRSW). When compared with six grain shape and size traits, the quality traits showed mostly independent genetic control (~18% common loci), while the yield traits showed moderate association (~53% common loci). Association of genomic regions for grain area (GA) and thousand-grain weight (TGW), with yield suggests that targeting an increase in GA may help enhancing wheat yield through an increase in TGW. Flour extraction (FE), although has a weak positive phenotypic association with grain shape and size, they do not share any common genetic loci. A major contributor to plant height was the Rht8 locus and the reduced height allele was associated with significant increase in grains per spike (GPS) and FE, and decrease in number of spikes per square meter and test weight. Stable loci were identified for almost all the traits. However, we could not find any QTL in the region of major known genes like GPC-B1, Ha, Rht-1, and Ppd-1. Epistasis also played an important role in the genetics of majority of the traits. In addition to enhancing our knowledge about the association of wheat quality and yield with grain shape and size, this study provides novel loci, genetic information and pre-breeding material (combining positive alleles from both parents) to enhance the cultivated gene pool in wheat germplasm. These resources are valuable in facilitating molecular breeding for wheat quality and yield improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exotic QTL improve grain quality in the tri-parental wheat population SW84.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 7;12(7):e0179851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179851. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28686676 Free PMC article.
-
QTL mapping for grain yield-related traits in bread wheat via SNP-based selective genotyping.Theor Appl Genet. 2020 Mar;133(3):857-872. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03511-0. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Theor Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 31844965
-
Identification and fine mapping of a QTL-rich region for yield- and quality-related traits on chromosome 4BS in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Sep 28;137(10):239. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04722-w. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 39342035
-
Genetic architecture underpinning yield component traits in wheat.Theor Appl Genet. 2020 Jun;133(6):1811-1823. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03562-8. Epub 2020 Feb 15. Theor Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 32062676 Review.
-
Genetic identification and characterization of quantitative trait loci for wheat grain size-related traits independent of grain number per spike.Theor Appl Genet. 2025 May 25;138(6):125. doi: 10.1007/s00122-025-04912-0. Theor Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 40413655 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic dissection of value-added quality traits and agronomic parameters through genome-wide association mapping in bread wheat (T. aestivum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 20;15:1419227. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1419227. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39228836 Free PMC article.
-
Toward the Genetic Basis and Multiple QTLs of Kernel Hardness in Wheat.Plants (Basel). 2020 Nov 24;9(12):1631. doi: 10.3390/plants9121631. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33255282 Free PMC article.
-
QTL analysis identified two major all-internodes solidness loci from a completely solid-stemmed spring wheat line.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 15;13:1035620. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1035620. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36457538 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide identification of QTL associated with yield and yield components in two popular wheat cultivars TAM 111 and TAM 112.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 2;15(12):e0237293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237293. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33264303 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Glu-D1 Alleles and Novel Marker-Trait Associations for Flour Quality and Grain Yield Traits under Heat-Stress Environments in Wheat Lines Derived from Diverse Accessions of Aegilops tauschii.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12034. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912034. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kulwal P, Kumar N, Kumar A, Balyan HS, Gupta PK. Gene networks in hexaploid wheat: interacting quantitative trait loci for grain protein content. Funct Integr Genomic. 2005; 5:254–259. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Elias EM, Gavami F, Xu X, Jain S, Manthey FA, et al. A major QTL for gluten strength in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum). J Cereal Science. 2013; 57: 21–29.
-
- Oury F, Chiron H, Pichon M, Giraud A, Bérard P, Faye A, et al. Reliability of indirect selection in determining the quality of bread wheat for French bread-baking. Agronomie. 1999; 19: 621–634.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

