Influence of UiO-66(Zr) Preparation Strategies in Its Catalytic Efficiency for Desulfurization Process
- PMID: 31533221
- PMCID: PMC6766325
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12183009
Influence of UiO-66(Zr) Preparation Strategies in Its Catalytic Efficiency for Desulfurization Process
Abstract
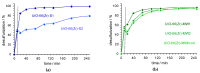
Porous metal-organic framework (MOF) materials UiO-66(Zr) obtained by solvothermal and microwave advanced synthesis (MWAS) procedures were characterized, and their catalytic efficiency was investigated for oxidative desulfurization (ODS) processes using a multicomponent model diesel containing benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene derivatives. The preparation parameters as the cooling time after oven use in the solvothermal procedure, and also the reaction time in the MWAS method seemed to play an important role in the catalytic performance of the UiO-66(Zr) material, as well as in its recycle capacity. The material prepared by the solvothermal procedure with a fast cooling time showed the best catalytic performance (desulfurization efficiency of 99.5% after 3 h). However, the application of the UiO-66(Zr) material prepared by the MWAS method (desulfurization efficiency of 96% after 3 h) conciliated a higher number of advantages, such as shorter reaction time preparation (15 min) and high catalytic activity for a higher number of reaction cycles. The UiO-66(Zr) prepared by the MWAS method was used for the first time in an oxidative desulfurization process, and according to the catalytic results obtained (high recycle capacity and stability) and shorter reaction time preparation, seems to be a promising material for industrial application.
Keywords: UiO-66(Zr); heterogeneous catalysis; microwave assisted synthesis; oxidative desulfurization; porous metal-organic frameworks; solvothermal synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Fox E.B., Liu Z.-W., Liu Z.-T. Ultraclean fuels production and utilization for the twenty-first century: Advances toward sustainable transportation fuels. Energy Fuels. 2013;27:6335–6338. doi: 10.1021/ef401094t. - DOI
-
- Srivastava V.C. An evaluation of desulfurization technologies for sulfur removal from liquid fuels. RSC Adv. 2012;2:759–783. doi: 10.1039/C1RA00309G. - DOI
-
- Babich I.V., Moulijn J.A. Science and technology of novel processes for deep desulfurization of oil refinery streams: A review. Fuel. 2003;82:607–631. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00324-1. - DOI
-
- Ibrahim M.H., Hayyan M., Hashim M.A., Hayyan A. The role of ionic liquids in desulfurization of fuels: A. review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017;76:1534–1549. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.194. - DOI
-
- Campos-Martin J.M., Capel-Sanchez M.C., Perez-Presas P., Fierro J.L.G. Oxidative processes of desulfurization of liquid fuels. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010;85:879–890. doi: 10.1002/jctb.2371. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

