Liquid biopsies in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 31533487
- PMCID: PMC6824837
- DOI: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1670063
Liquid biopsies in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
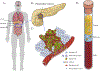
Introduction: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a disease of high lethality. Invasive tissue biopsies of primary or metastatic lesions remain the gold standard for diagnosis, but repeated sampling is infeasible. Noninvasive liquid biopsies offer new opportunities for early diagnosis for high-risk cohorts, and for the longitudinal analysis of tumor evolution and progression in patients on therapy. Liquid biopsies can capture tumor-associated components, such as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), extracellular vesicles (EVs), and circulating tumor cells (CTCs), each of which provides genomic and molecular information about the underlying PDAC that can potentially inform clinical decisions. Areas covered: Here, we reviewed current knowledge and recent technological advances regarding liquid biopsy in PDAC and mention the pitfalls and benefits in each methodology. We also discuss clinical correlative studies for diagnosis and prognosis in PDAC. Expert opinion:In pancreatic cancer where tissue samples are limited and repeated tissue biopsies are mostly invasive and infeasible, liquid biopsies opened a new window for tumor diagnosis, molecular stratification, and treatment monitoring. While none of the isolation and analysis methods have gained widespread clinical acceptance, it is imperative that the advantages and limitations of each platform for isolation and analysis of tumor associated components are taken into consideration.
Keywords: Cell-free DNA; circulating tumor cells; extracellular vesicles; liquid biopsies; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
Anirban Maitra has received royalties from Cosmos Wisdom Biotechnology Company LTD for being a co-inventor on a license related to pancreatic cancer early detection, and this financial relationship is managed by the MD Anderson Conflict of Interest Committee. Editorial assistance was provided by Joseph Munch, Department of Scientific Publications, UT MD Anderson Cancer Center. There are no other conflicts of interests to declare. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
