Impact of combination HIV interventions on HIV incidence in hyperendemic fishing communities in Uganda: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 31533894
- PMCID: PMC6832692
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30190-0
Impact of combination HIV interventions on HIV incidence in hyperendemic fishing communities in Uganda: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Targeting combination HIV interventions to locations and populations with high HIV burden is a global priority, but the impact of these strategies on HIV incidence is unclear. We assessed the impact of combination HIV interventions on HIV incidence in four HIV-hyperendemic communities in Uganda.
Methods: We did an open population-based cohort study of people aged 15-49 years residing in four fishing communities on Lake Victoria. The communities were surveyed five times to collect self-reported demographic, behavioural, and service-uptake data. Free HIV testing was provided at each interview, with referral to combination HIV intervention services as appropriate. From November, 2011, combination HIV intervention services were rapidly expanded in these geographical areas. We evaluated trends in HIV testing coverage among all participants, circumcision coverage among male participants, antiretroviral therapy (ART) coverage and HIV viral load among HIV-positive participants, and sexual behaviours and HIV incidence among HIV-negative participants.
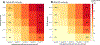
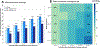
Findings: From Nov 4, 2011, to Aug 16, 2017, data were collected from five surveys. Overall, 8942 participants contributed 20 721 person-visits; 4619 (52%) of 8942 participants were male. HIV prevalence was 41% (1598 of 3870) in the 2011-12 baseline survey and declined to 37% (1740 of 4738) at the final survey (p<0·0001). 3222 participants who were HIV-negative at baseline, and who had at least one repeat visit, contributed 9477 person-years of follow-up, and 230 incident HIV infections occurred. From the first survey in 2011-12 to the last survey in 2016-17, HIV testing coverage increased from 68% (2613 of 3870) to 96% (4526 of 4738; p<0·0001); male circumcision coverage increased from 35% (698 of 2011) to 65% (1630 of 2525; p<0·0001); ART coverage increased from 16% (254 of 1598) to 82% (1420 of 1740; p<0·0001); and population HIV viral load suppression in all HIV-positive participants increased from 34% (546 of 1596) to 80% (1383 of 1734; p<0·0001). Risky sexual behaviours did not decrease over this period. HIV incidence decreased from 3·43 per 100 person-years (95% CI 2·45-4·67) in 2011-12 to 1·59 per 100 person-years (95% CI 1·19-2·07) in 2016-17; adjusted incidence rate ratio (IRR) 0·52 (95% CI 0·34-0·79). Declines in HIV incidence were similar among men (adjusted IRR 0·53, 95% CI 0·30-0·93) and women (0·51, 0·27-0·96). The risk of incident HIV infection was lower in circumcised men than in uncircumcised men (0·46, 0·32-0·67).
Interpretation: Rapid expansion of combination HIV interventions in HIV-hyperendemic fishing communities is feasible and could have a substantial impact on HIV incidence. However, incidence remains higher than HIV epidemic control targets, and additional efforts will be needed to achieve this global health priority.
Funding: The National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Child Health and Development, the National Cancer Institute, the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases Division of Intramural Research, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Uganda, Karolinska Institutet, and the Johns Hopkins University Center for AIDS Research.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest
We declare that we have nothing to disclose.
Figures
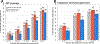
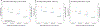
Comment in
-
HIV control in hyperendemic communities in east Africa.Lancet HIV. 2019 Oct;6(10):e643-e644. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30241-3. Epub 2019 Sep 15. Lancet HIV. 2019. PMID: 31533895 No abstract available.
References
-
- PEPFAR 2018 Annual Report to Congress. The Office of the U.S. Global AIDS Coordinator and Health Diplomacy. April 2018. http://www.pepfar.gov/documents/organization/234744.pdf. Last access date: April 30, 2019.
-
- UNAIDS. Global AIDS Update 2017. Geneva, Switzerland: United National Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI100031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107275/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI075115/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143333/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI102939/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105313/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW010557/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI125086/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI128779/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI110324/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD091003/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

