Silicon isotopes in Arctic and sub-Arctic glacial meltwaters: the role of subglacial weathering in the silicon cycle
- PMID: 31534420
- PMCID: PMC6735475
- DOI: 10.1098/rspa.2019.0098
Silicon isotopes in Arctic and sub-Arctic glacial meltwaters: the role of subglacial weathering in the silicon cycle
Abstract
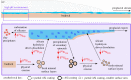
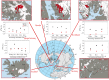
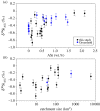
Glacial environments play an important role in high-latitude marine nutrient cycling, potentially contributing significant fluxes of silicon (Si) to the polar oceans, either as dissolved silicon (DSi) or as dissolvable amorphous silica (ASi). Silicon is a key nutrient in promoting marine primary productivity, contributing to atmospheric CO2 removal. We present the current understanding of Si cycling in glacial systems, focusing on the Si isotope (δ30Si) composition of glacial meltwaters. We combine existing glacial δ30Si data with new measurements from 20 sub-Arctic glaciers, showing that glacial meltwaters consistently export isotopically light DSi compared with non-glacial rivers (+0.16‰ versus +1.38‰). Glacial δ30SiASi composition ranges from -0.05‰ to -0.86‰ but exhibits low seasonal variability. Silicon fluxes and δ30Si composition from glacial systems are not commonly included in global Si budgets and isotopic mass balance calculations at present. We discuss outstanding questions, including the formation mechanism of ASi and the export of glacial nutrients from fjords. Finally, we provide a contextual framework for the recent advances in our understanding of subglacial Si cycling and highlight critical research avenues for assessing potential future changes in these environments.
Keywords: glaciers and ice sheets; silicon cycle; silicon isotopes; subglacial weathering.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hawkings JR, et al. 2015. The effect of warming climate on nutrient and solute export from the Greenland Ice Sheet. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 1, 94–104. ( 10.7185/geochemlet.1510) - DOI
-
- Lawson EC, et al. 2014. Greenland Ice Sheet exports labile organic carbon to the Arctic oceans. Biogeosciences 11, 4015–4028. ( 10.5194/bg-11-4015-2014) - DOI
-
- Meire L, et al. 2016. High export of dissolved silica from the Greenland Ice Sheet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 9173–9182. ( 10.1002/2016GL070191) - DOI
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
