Contributions of GRACE to understanding climate change
- PMID: 31534490
- PMCID: PMC6750016
- DOI: 10.1038/s41558-019-0456-2
Contributions of GRACE to understanding climate change
Abstract
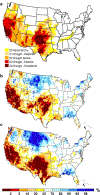
Time-resolved satellite gravimetry has revolutionized understanding of mass transport in the Earth system. Since 2002, the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) has enabled monitoring of the terrestrial water cycle, ice sheet and glacier mass balance, sea level change and ocean bottom pressure variations and understanding responses to changes in the global climate system. Initially a pioneering experiment of geodesy, the time-variable observations have matured into reliable mass transport products, allowing assessment and forecast of a number of important climate trends and improve service applications such as the U.S. Drought Monitor. With the successful launch of the GRACE Follow-On mission, a multi decadal record of mass variability in the Earth system is within reach.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
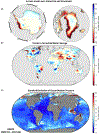
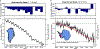
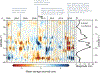
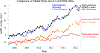
References
-
- Tapley BD, Bettadpur S, Watkins M & Reigber C The gravity recovery and climate experiment: Mission overview and early results. Geophys. Res. Lett 31, (2004).
-
- National Research Council. Satellite gravity and the geosphere: contributions to the study of the solid Earth and its fluid envelopes. (National Academies Press, 1997).
-
- Marti U Gravity, Geoid and Height Systems: Proceedings of the IAG Symposium GGHS2012, October 9–12, 2012, Venice, Italy: 141, (Springer, 2015).
-
- Save H, Bettadpur S & Tapley BD High-resolution CSR GRACE RL05 mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 121, 7547–7569 (2016).
-
- Luthcke SB et al. Recent Greenland ice mass loss by drainage system from satellite gravity observations. Science 314, 1286–1289 (2006). - PubMed
