Prostaglandin E2 induces DNA hypermethylation in gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 31534549
- PMCID: PMC6735505
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.35766
Prostaglandin E2 induces DNA hypermethylation in gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
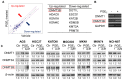
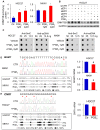
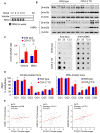
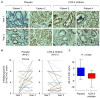
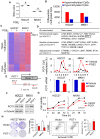
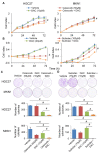
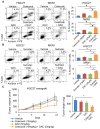
Rationale: Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is a pro-inflammatory eicosanoid up-regulated in gastric cancer (GC). However, its impact on epigenetic dysfunction in the process of gastric carcinogenesis is unknown. In this study, we investigate the role of PGE2 in DNA methylation in gastric epithelium in vitro, in mice, and humans. Methods: PGE2-induced DNMT3B and DNA methylation was determined in gastric cell lines and COX-2 transgenic mice. Effect of COX-2 inhibition on DNA methylation was evaluated in a randomized controlled trial. Efficacy of combined COX-2/PGE2 and DNMT inhibition on GC growth was examined in cell lines and mice models. Results: PCR array analysis of PGE2-treated GC cells revealed the up-regulation of DNMT3B, a de novo DNA methyltransferase. In GC cells, PGE2 induced DNMT3B expression and activity, leading to increased methylated cytosine (5mC) and promoter methylation of tumor suppressive genes (MGMT and CNR1). Consistently, Cox-2 (rate-limiting enzyme for PGE2 biosynthesis) transgenic expression in mice significantly induced Dnmt3b expression, increased 5mC content, and promoted Mgmt promoter methylation. We retrospectively analyzed the 5mC content of 42 patients with intestinal metaplasia (a precancerous lesion of GC) treated with a COX-2 specific inhibitor Rofecoxib or placebo for 2 years, revealing that the COX-2 inhibitor significantly down-regulated 5mC levels (N=42, P=0.009). Collectively, these data indicate that PGE2 is closely related to DNA hypermethylation in vitro and in vivo. Using genome-wide 450K methylation array, we identified chromosomal genes (POT1, ATM and HIST1H2AA) were preferentially methylated by PGE2. Biofunctional work revealed that POT1 functions as a tumor suppressor. Finally, we demonstrated that combinatorial inhibition of COX-2 and DNMT using Celecoxib and Decitabine synergistically inhibited GC growth in vitro and in vivo. Conclusion: This study suggested that PGE2 promotes DNA methylation in GC, and that co-targeting of PGE2 and DNMT inhibits GC.
Keywords: COX-2 transgenic mice; DNA methylation; DNMT3B; Gastric cancer; Prostaglandin E2.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Verdecchia A, Corazziari I, Gatta G, Lisi D, Faivre J, Forman D. Explaining gastric cancer survival differences among European countries. Int J Cancer. 2004;109:737–41. - PubMed
-
- Bertuccio P, Chatenoud L, Levi F, Praud D, Ferlay J, Negri E. et al. Recent patterns in gastric cancer: a global overview. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:666–73. - PubMed
-
- Mrena J, Wiksten JP, Kokkola A, Nordling S, Ristimaki A, Haglund C. COX-2 is associated with proliferation and apoptosis markers and serves as an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2010;31:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Lim HY, Joo HJ, Choi JH, Yi JW, Yang MS, Cho DY. et al. Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 protein in human gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:519–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

