Anticancer activity of metformin: a systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 31534778
- PMCID: PMC6745597
- DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2019-0053
Anticancer activity of metformin: a systematic review of the literature
Abstract
Background: The anticancer activity of metformin has been confirmed against several cancer types in vitro and in vivo. However, the underlying mechanisms of metformin in the treatment of cancer are not fully understood. This systematic review aims to discuss the possible anticancer mechanism of action of metformin.
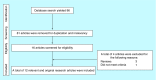
Method: A search through different databases was conducted, including Medline and EMBASE.
Results: A total of 96 articles were identified of which 56 were removed for duplication and 24 were excluded after reviewing the title and abstract. A total of 12 research articles were included that describe different antiproliferative mechanisms that may contribute to the antineoplastic effects of metformin.
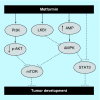
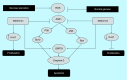
Conclusion: This analysis discussed the potential anticancer activity of metformin and highlighted the importance of AMPK as a potential target for anticancer therapy.
Keywords: AMPK; anticancer; cancer; mechanism of action; metformin.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Aljofan M, Ding H. High glucose increases expression of cyclooxygenase-2, increases oxidative stress and decreases the generation of nitric oxide in mouse microvessel endothelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 222(3), 669–675 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Ding H, Aljofan M, Triggle CR. Oxidative stress and increased eNOS and NADPH oxidase expression in mouse microvessel endothelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 212(3), 682–689 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Reinehr T, Kiess W, Kapellen T, Andler W. Insulin sensitivity among obese children and adolescents, according to degree of weight loss. Pediatrics 114(6), 1569–1573 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Wexler DJ. Initial management of blood glucose in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nathan MD. (Ed.). UpToDate (2019).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
