False rifampicin resistant results using Xpert MTB/RIF on urine samples in hospitalised HIV-infected patients
- PMID: 31534789
- PMCID: PMC6739559
- DOI: 10.4102/sajhivmed.v20i1.978
False rifampicin resistant results using Xpert MTB/RIF on urine samples in hospitalised HIV-infected patients
Abstract
Background: A small proportion of false rifampicin resistant results have previously been reported using GeneXpert MTB/RIF version G4 on sputum samples; however, this has not been investigated for urine samples in HIV-associated tuberculosis (TB).
Objectives: We sought to determine the proportion of false rifampicin resistant results using Xpert MTB/RIF version G4 on urine samples among HIV-infected inpatients investigated for TB.
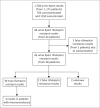
Methods: Hospitalised HIV-infected patients undergoing systematic TB testing from two cohorts in Cape Town, South Africa, were enrolled. All patients with ≥1 urine Xpert result available were included. Rifampicin resistant urine Xpert results were classified into three mutually exclusive groups: (1) true rifampicin resistance, (2) false rifampicin resistance or (3) unknown after review of available microbiologic and clinical data.
Results: Overall, 1171 patients were included, from whom a total of 1704 urine Xpert results were available on unconcentrated and/or concentrated urine samples. There were 416 samples positive for TB (24.4% [95% CI 22.4-26.5]), of which 43/413 (10.4% [95% CI 7.6-13.8]) were rifampicin resistant (after excluding three results that were falsely positive due to contamination). Of 43 rifampicin resistant Xpert results (among 40 patients), 30 were classified as true resistance, 11 as false resistance and 2 could not be classified. Excluding unclassifiable results, 30/41 results were confirmed as true-positive urine Xpert rifampicin resistance (positive predictive value: 73.2% [95% CI 57.1-85.8]).
Conclusion: Urine Xpert testing showed a high proportion of false rifampicin resistance results. Urine Xpert rifampicin resistant results should be interpreted cautiously and confirmed when possible.
Keywords: AIDS; False resistance; HIV; Rifampicin resistance; Tuberculosis; Xpert.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2016. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- Organization WH. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources