Ceftriaxone use in brucellosis: A case series
- PMID: 31534908
- PMCID: PMC6744365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00633
Ceftriaxone use in brucellosis: A case series
Abstract
Background: Brucellosis is a zoonotic disease caused by Brucella spp. It can be either uncomplicated or complicated when it disseminates to other organs. Treatment for brucellosis involves a combination of at least two antibiotics, or more in complicated brucellosis. Limited data exist on the use of ceftriaxone in the clinical setting. Therefore, we present patient cases in which ceftriaxone was used in brucellosis treatment regimen.
Methods: Patients with documented brucellosis from January 2008 to December 2018 were evaluated for the use of ceftriaxone for treatment in King Abdulaziz Univeristy Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Patients' data were evaluated retrospectively and are described.
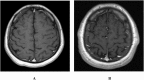
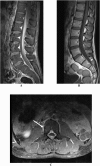
Results: Out of 94 treated brucellosis patients, six patients received ceftriaxone 2 g IV every 12 h for therapy for varied durations. Four had neurobrucellosis, one had Brucella epididymo-orchitis and one had uncomplicated brucellosis. All six patients experienced clinical cure, though one neurobrucellosis patient had complications and one had ceftriaxone stopped after one week of therapy due to presumed antibiotic-induced fever.
Conclusion: Ceftriaxone represents a reasonable option for the treatment of complicated brucellosis when added to the initial regimen at a dose of 2 g IV every 12 h.
Keywords: Brucella; Brucellosis; Cases; Ceftriaxone; Saudi Arabia; Zoonotic infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brucellar epididymo-orchitis in Saudi Arabia: a retrospective study of 26 cases and review of the literature.BJU Int. 2001 Jul;88(1):72-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02243.x. BJU Int. 2001. PMID: 11446850 Review.
-
Dual versus triple therapy for uncomplicated brucellosis: A retrospective cohort study.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020 Dec 31;14(12):1380-1386. doi: 10.3855/jidc.12741. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020. PMID: 33378279
-
Human brucellosis in Northern Saudi Arabia.Saudi Med J. 2005 Oct;26(10):1562-6. Saudi Med J. 2005. PMID: 16228056
-
Manifestations, complications, and treatment of neurobrucellosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Neurosci. 2024 Jun;134(3):256-266. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2022.2100776. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Int J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 35930502
-
Brucella epididymo-orchitis: a consideration in endemic area.Int Braz J Urol. 2006 May-Jun;32(3):313-5. doi: 10.1590/s1677-55382006000300011. Int Braz J Urol. 2006. PMID: 16813677
Cited by
-
Brucellosis Presenting With Pancytopenia and Foot Drop.Cureus. 2020 Sep 7;12(9):e10293. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10293. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33047083 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Neurobrucellosis Presenting as Malignancy.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024 Jun 11;111(2):312-316. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0684. Print 2024 Aug 7. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024. PMID: 38861982 Free PMC article.
-
Brucella epidydimo-orchitis successfully treated with dual oral drug regimen: A case report with differential diagnoses of malignancy and tuberculosis.Radiol Case Rep. 2022 Jul 27;17(10):3485-3489. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.07.012. eCollection 2022 Oct. Radiol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35912293 Free PMC article.
-
The current therapeutical strategies in human brucellosis.Infection. 2021 Oct;49(5):823-832. doi: 10.1007/s15010-021-01586-w. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Infection. 2021. PMID: 33650077 Review.
-
Brucellosis: Unveiling the complexities of a pervasive zoonotic disease and its global impacts.Open Vet J. 2024 May;14(5):1081-1097. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i5.1. Epub 2024 May 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 38938422 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Corbel M.J. World Health Organization; 2006. Brucellosis in humans and animals.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 2017. Brucellosis reference guide: exposures, testing and prevention.
-
- Tuon F.F., Cerchiari N., Cequinel J.C., Droppa E.E.H., Moreira S.D.R., Costa T.P. Guidelines for the management of human brucellosis in the State of Paraná, Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017;50:458–464. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

