Heterotopic Ossification following Suprapatellar Intramedullary Nailing
- PMID: 31534925
- PMCID: PMC6727441
- DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.1348
Heterotopic Ossification following Suprapatellar Intramedullary Nailing
Abstract
Introduction: Tibial shaft fractures are common fractures seen in trauma and orthopedic practice today. The majority of these fractures are treated with intramedullary nailing (IMN) which is rapidly becoming a gold standard. The procedure itself is performed by either a suprapatellar approach or infrapatellar approach. Suprapatellar approach is gaining popularity due to relative ease of insertion, decreased associated risk of anterior knee pain, and more accurate reduction. We report a case of heterotopic ossification noted in the knee following IMN of tibia performed using a suprapatellar approach.
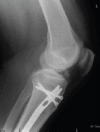
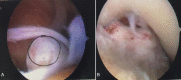
Case report: A 27-year-old male, having sustained a left, Gustilo IIIB tibial shaft fracture following a motor vehicle accident, underwent a reamed intramedullary nail fixation performed through a suprapatellar approach. Two months later, he presented with intra-articular heterotopic ossification which was limiting his knee movement. He then underwent arthroscopic removal of the bony fragments which resolved his symptoms.
Conclusion: An extensive search of literature did not yield any reported incidence of heterotopic ossification associated with IMN performed through a suprapatellar approach. We present this case report to raise awareness that although IMN through a suprapatellar approach is a safe approach, it does have associated risk of heterotopic ossification which needs to be included in the consent process.
Keywords: Heterotopic ossification; Intramedullary nailing; Suprapatellar approach; Tibial shaft fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Figures
References
-
- Larsen P, Elsoe R, Hansen SH, Graven-Nielsen T, Laessoe U, Rasmussen S. Incidence and epidemiology of tibial shaft fractures. Injury. 2015;46:746–50. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Chen E, Ye C, Pan Z. Suprapatellar versus infrapatellar approach for tibia intramedullary nailing:A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;51:133–9. - PubMed
-
- Katsoulis E, Court-Brown C, Giannoudis PV. Incidence and aetiology of anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of the femur and tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:576–80. - PubMed
-
- Jones M, Parry M, Whitehouse M, Mitchell S. Radiologic outcome and patient-reported function after intramedullary nailing:A comparison of the retropatellar and infrapatellar approach. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28:256–62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources