Claudin-15 overexpression inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of Schwann cells in vitro
- PMID: 31535666
- PMCID: PMC6862392
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.264463
Claudin-15 overexpression inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of Schwann cells in vitro
Abstract
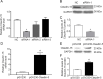
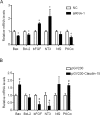
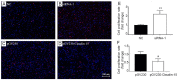
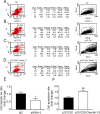
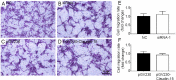
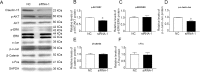
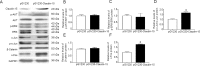
Our previous experiments have discovered that Claudin-15 was up-regulated in Schwann cells of the distal nerve stumps of rat models of sciatic nerve injury. However, how Claudin-15 affects Schwann cell function is still unknown. This study aimed to identify the effects of Claudin-15 on proliferation and apoptosis of Schwann cells cultured in vitro and explore the underlying mechanisms. Primary Schwann cells were obtained from rats. Claudin-15 in Schwann cells was knocked down using siRNA (siRNA-1 group) compared with the negative control siRNA transfection group (negative control group). Claudin-15 in Schwann cells was overexpressed using pGV230-Claudin-15 plasmid (pGV230-Claudin-15 group). The pGV230 transfection group (pGV230 group) acted as the control of the pGV230-Claudin-15 group. Cell proliferation was analyzed with EdU assay. Cell apoptosis was analyzed with flow cytometric analysis. Cell migration was analyzed with Transwell inserts. The mRNA and protein expressions were analyzed with quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay and western blot assay. The results showed that compared with the negative control group, cell proliferation rate was up-regulated; p-AKT/AKT ratio, apoptotic rate, p-c-Jun/c-Jun ratio, mRNA expression of protein kinase C alpha, Bcl-2 and Bax were down-regulated; and mRNA expression of neurotrophins basic fibroblast growth factor and neurotrophin-3 were increased in the siRNA-1 group. No significant difference was found in cell migration between the negative control and siRNA-1 groups. Compared with the pGV230 group, the cell proliferation rate was down-regulated; apoptotic rate, p-c-Jun/c-Jun ratio and c-Fos protein expression increased; mRNA expression of protein kinase C alpha and Bax decreased; and mRNA expressions of neurotrophins basic fibroblast growth factor and neurotrophin-3 were up-regulated in the pGV230-Claudin-15 group. The above results demonstrated that overexpression of Claudin-15 inhibited Schwann cell proliferation and promoted Schwann cell apoptosis in vitro. Silencing of Claudin-15 had the reverse effect and provided neuroprotective effect. This study was approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University of China (approval No. 2016-nsfc001) on March 5, 2016.
Keywords: Bax; Claudin-15; Schwann cells; Wallerian degeneration; apoptosis; c-Jun; cell proliferation; nerve regeneration; peripheral nerve injury; protein kinase C alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Alberini G, Benfenati F, Maragliano L. Molecular dynamics simulations of ion selectivity in a claudin-15 paracellular channel. J Phys Chem B. 2018 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b06484. - PubMed
-
- Bi C, Cai Q, Shan Y, Yang F, Sun S, Wu X, Liu H. Sevoflurane induces neurotoxicity in the developing rat hippocampus by upregulating connexin 43 via the JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1469–1476. - PubMed
-
- Cao P, Wang HN, Tian WF, Sun NC, Bai JB, Yu KL, Tian DH. Human amniotic membrane repairs acute sciatic nerve injury in rat models. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2019;23:1046–1051.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

