Electrochemical Detection of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Nanointerdigitated Electrodes
- PMID: 31536360
- PMCID: PMC7020140
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b02741
Electrochemical Detection of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Nanointerdigitated Electrodes
Abstract
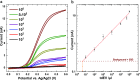
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (tdEVs) are attracting much attention due to their essential function in intercellular communication and their potential as cancer biomarkers. Although tdEVs are significantly more abundant in blood than other cancer biomarkers, their concentration compared to other blood components remains relatively low. Moreover, the presence of particles in blood with a similar size as that of tdEVs makes their selective and sensitive detection further challenging. Therefore, highly sensitive and specific biosensors are required for unambiguous tdEV detection in complex biological environments, especially for decentralized point-of-care analysis. Here, we report an electrochemical sensing scheme for tdEV detection, with two-level selectivity provided by a sandwich immunoassay and two-level amplification through the combination of an enzymatic assay and redox cycling on nanointerdigitated electrodes to respectively enhance the specificity and sensitivity of the assay. Analysis of prostate cancer cell line tdEV samples at various concentrations revealed an estimated limit of detection for our assay as low as 5 tdEVs/μL, as well as an excellent linear sensor response spreading over 6 orders of magnitude (10-106 tdEVs/μL), which importantly covers the clinically relevant range for tdEV detection in blood. This novel nanosensor and associated sensing scheme opens new opportunities to detect tdEVs at clinically relevant concentrations from a single blood finger prick.
Keywords: Nanoelectrodes; enzymatic amplification; microfluidics; redox cycling; tumor-derived extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electrochemical detection and analysis of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles to evaluate malignancy of pancreatic cystic neoplasm using integrated microfluidic device.Biosens Bioelectron. 2023 Apr 15;226:115124. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115124. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023. PMID: 36758487
-
HER2 expression on tumor-derived extracellular vesicles and circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Aug 12;22(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01323-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32787900 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of extracellular vesicles in plasma and urine of prostate cancer patients by flow cytometry and surface plasmon resonance imaging.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 4;15(6):e0233443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233443. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32497056 Free PMC article.
-
Signal amplification strategies in biosensing of extracellular vesicles (EVs).Talanta. 2023 May 1;256:124244. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.124244. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 36640707 Review.
-
Toward Personalized Cancer Treatment: From Diagnostics to Therapy Monitoring in Miniaturized Electrohydrodynamic Systems.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Aug 20;52(8):2113-2123. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00192. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31293158 Review.
Cited by
-
Mixed-Dimensional Heterostructure Material-Based SERS for Trace Level Identification of Breast Cancer-Derived Exosomes.ACS Omega. 2020 Jul 1;5(27):16602-16611. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01441. eCollection 2020 Jul 14. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32685826 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and patient monitoring.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020 Apr;20(4):387-400. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2020.1731308. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020. PMID: 32067543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Nanotechnologies for Extracellular Vesicle-Based Liquid Biopsy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Oct;8(20):e2102789. doi: 10.1002/advs.202102789. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34463056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal Biomarkers: A Comprehensive Overview of Diagnostic and Prognostic Applications in Malignant and Non-Malignant Disorders.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 15;15(4):587. doi: 10.3390/biom15040587. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of extracellular vesicles in major depressive disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Mar 9;14:1138110. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1138110. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36970289 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nanou A.; Coumans F. A.; van Dalum G.; Zeune L. L.; Dolling D.; Onstenk W.; Crespo M.; Fontes M. S.; Rescigno P.; Fowler G.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, tumor-derived extracellular vesicles and plasma cytokeratins in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Oncotarget 2018, 9 (27), 19283.10.18632/oncotarget.25019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Budd G. T.; Cristofanilli M.; Ellis M. J.; Stopeck A.; Borden E.; Miller M. C.; Matera J.; Repollet M.; Doyle G. V.; Terstappen L. W.; et al. Circulating tumor cells versus imaging—predicting overall survival in metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12 (21), 6403–6409. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1769. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

