Suppressive impact of metronomic chemotherapy using UFT and/or cyclophosphamide on mediators of breast cancer dissemination and invasion
- PMID: 31536574
- PMCID: PMC6752870
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222580
Suppressive impact of metronomic chemotherapy using UFT and/or cyclophosphamide on mediators of breast cancer dissemination and invasion
Abstract
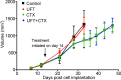
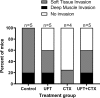
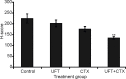
Metronomic chemotherapy using the 5-FU prodrug uracil-tegafur (UFT) and cyclophosphamide (CTX) was previously shown to only modestly delay primary tumor growth, but nevertheless markedly suppressed the development of micro-metastasis in an orthotopic breast cancer xenograft model, using the metastatic variant of the MDA-MB-231 cell line, 231/LM2-4. Furthermore, a remarkable prolongation of survival, with no toxicity, was observed in a model of postsurgical advanced metastatic disease. A question that has remained unanswered is the seemingly selective anti-metastatic mechanisms of action responsible for this treatment. We assessed the in vivo effect of metronomic UFT, CTX or their combination, on vascular density, collagen deposition and c-Met (cell mediators or modulators of tumor cell invasion or dissemination) via histochemistry/immunohistochemistry of primary tumor sections. We also assessed the effect of continuous exposure to low and non-toxic doses of active drug metabolites 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide (4-HC) or their combination, on 231/LM2-4 cell invasiveness in vitro. In the in vivo studies, a significant reduction in vascular density and p-Met[Y1003] levels was associated with UFT+CTX treatment. All treatments reduced intratumoral collagen deposition. In the in vitro studies, a significant reduction of collagen IV invasion by all treatments was observed. The 3D structures formed by 231/LM2-4 on Matrigel showed a predominantly Mass phenotype under treated conditions and Stellate phenotype in untreated cultures. Taken together, the results suggest the low-dose metronomic chemotherapy regimens tested can suppress several mediators of tumor invasiveness highlighting a new perspective for the anti-metastatic efficacy of metronomic chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Highly efficacious nontoxic preclinical treatment for advanced metastatic breast cancer using combination oral UFT-cyclophosphamide metronomic chemotherapy.Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 1;66(7):3386-91. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4411. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16585158
-
Impact of metronomic UFT/cyclophosphamide chemotherapy and antiangiogenic drug assessed in a new preclinical model of locally advanced orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma.Neoplasia. 2010 Mar;12(3):264-74. doi: 10.1593/neo.91872. Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20234820 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose metronomic oral dosing of a prodrug of gemcitabine (LY2334737) causes antitumor effects in the absence of inhibition of systemic vasculogenesis.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Mar;11(3):680-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0659. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22188817 Free PMC article.
-
UFT and leucovorin: a review of its clinical development and therapeutic potential in the oral treatment of cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 1998 Jul;9(6):479-90. Anticancer Drugs. 1998. PMID: 9877235 Review.
-
Epirubicin, cyclophosphamide, and UFT plus oral calcium folinate in advanced breast cancer.Oncology (Williston Park). 1999 Jul;13(7 Suppl 3):82-5. Oncology (Williston Park). 1999. PMID: 10442370 Review.
Cited by
-
Adjuvant Metronomic Chemotherapy After Surgery in pT1-T2 N0 M0 HER2-Positive and ER/PR-Positive Breast Cancer Plus Targeted Therapy, Anti-Hormonal Therapy, and Radiotherapy, with or Without Immunotherapy: A New Operational Proposal.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;17(8):1323. doi: 10.3390/cancers17081323. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282499 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose metronomic chemotherapy as an efficient treatment option in metastatic breast cancer-results of an exploratory case-control study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jul;182(2):389-399. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05711-5. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32495001 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Plasma vs. Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 13;25(6):3254. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063254. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542225 Free PMC article.
-
Immunostimulatory and anti-tumor metronomic cyclophosphamide regimens assessed in primary orthotopic and metastatic murine breast cancer.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020 Jul 20;6:29. doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-0171-1. eCollection 2020. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32704531 Free PMC article.
-
Co-targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells and endothelial cells by metronomic chemotherapy inhibits cell regrowth and migration via downregulation of the FAK/VEGFR2/VEGF axis and autophagy/apoptosis activation.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:998274. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.998274. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Marshall B, O'Reilly MS, Folkman J. Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1878–1886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

