Systemic treatments in MDM2 positive intimal sarcoma: A multicentre experience with anthracycline, gemcitabine, and pazopanib within the World Sarcoma Network
- PMID: 31536651
- PMCID: PMC9187112
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.32508
Systemic treatments in MDM2 positive intimal sarcoma: A multicentre experience with anthracycline, gemcitabine, and pazopanib within the World Sarcoma Network
Abstract
Background: Intimal sarcoma (InS) is an exceedingly rare neoplasm with an unfavorable prognosis, for which new potentially active treatments are under development. We report on the activity of anthracycline-based regimens, gemcitabine-based regimens, and pazopanib in patients with InS.
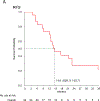
Methods: Seventeen sarcoma reference centers in Europe, the United States, and Japan contributed data to this retrospective analysis. Patients with MDM2-positive InS who were treated with anthracycline-based regimens, gemcitabine-based regimens, or pazopanib between October 2001 and January 2018 were selected. Local pathological review was performed to confirm diagnosis. Response was assessed by RECIST1.1. Recurrence-free survival (RFS), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival were computed by Kaplan-Meier method.
Results: Seventy-two patients were included (66 anthracycline-based regimens; 26 gemcitabine-based regimens; 12 pazopanib). In the anthracycline-based group, 24 (36%) patients were treated for localized disease, and 42 (64%) patients were treated for advanced disease. The real-world overall response rate (rwORR) was 38%. For patients with localized disease, the median RFS was 14.6 months. For patients with advanced disease, the median PFS was 7.7 months. No anthracycline-related cardiac toxicity was reported in patients with cardiac InS (n = 26). For gemcitabine and pazopanib, the rwORR was 8%, and the median PFS was 3.2 and 3.7 months, respectively.
Conclusion: This retrospective series shows the activity of anthracycline-based regimens in InS. Of note, anthracyclines were used in patients with cardiac InS with no significant cardiac toxicity. The prognosis in patients with InS remains poor, and new active drugs and treatment strategies are needed.
Keywords: MDM2; anthracycline; gemcitabine; intimal sarcoma; pazopanib; systemic therapies.
© 2019 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
AJW has reported consulting roles for Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Five Prime Therapeutics, Nanosphere; received honoraria from Novartis and institutional research support from Daiichi-Sankyo, Plexxikon, Eli Lilly, Aadi Bioscience, Five Prime Therapeutics, Karyopharm
Figures



References
-
- Fletcher CDMBJ, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone; Lyon, FR, IARC. 2013.
-
- Neuville A, Collin F, Bruneval P, et al. Intimal sarcoma is the most frequent primary cardiac sarcoma: clinicopathologic and molecular retrospective analysis of 100 primary cardiac sarcomas. The American journal of surgical pathology. Apr 2014;38(4):461–469. - PubMed
-
- Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13–14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology. Jan 2001;438(1):57–65. - PubMed
-
- Van Dievel J, Sciot R, Delcroix M, et al. Single-Center Experience with Intimal Sarcoma, an Ultra-Orphan, Commonly Fatal Mesenchymal Malignancy. Oncology research and treatment. 2017;40(6):353–359. - PubMed
-
- Kato W, Usui A, Oshima H, Suzuki C, Kato K, Ueda Y. Primary aortic intimal sarcoma. General thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. May 2008;56(5):236–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

