Helicobacter pylori recrudescence and its influencing factors
- PMID: 31536675
- PMCID: PMC6850920
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14682
Helicobacter pylori recrudescence and its influencing factors
Abstract
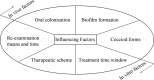
Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) is known as one of the most common infectious pathogens, with high infection and recurrence rates worldwide. The prevalence of H pylori is up to 90% in developing countries, while the annual recurrence rate is much higher than that in developed countries. Recurrence can occur either by recrudescence or reinfection. Compared with reinfection, the time window for recrudescence is generally shorter, followed by the recurrence of H pylori-associated diseases in the short-term. Many factors are involved in the H pylori reinfection, such as the prevalence of H pylori infection, living conditions and economic development, health conditions and so forth. Previous studies focused less on H pylori recrudescence. Therefore, the influencing factors for H pylori recrudescence needed further exploration. This study reviewed the recrudescence of H pylori infection and its influencing factors.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; colonization; influencing factors; recrudescence.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this study.
Figures
References
-
- Zeng M, Mao XH, Li JX, et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an oral recombinant Helicobacter pylori vaccine in children in China: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2015;386:1457‐1464. - PubMed
-
- Sarem M, Corti R. Role of Helicobacter pylori coccoid forms in infection and recrudescence. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;39:28‐35. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Zhao X, Lu X, Li Y. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and hematologic system diseases. Chin J Gastroenter Hepatol. 2018;27:134‐137.
-
- Sjomina O, Pavlova J, Niv Y, Leja M. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2018;23(Suppl 1):e12514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

