A perfect storm: fetal inflammation and the developing immune system
- PMID: 31537013
- PMCID: PMC7875080
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-019-0582-6
A perfect storm: fetal inflammation and the developing immune system
Abstract
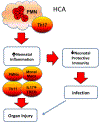
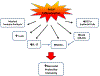
Histologic chorioamnionitis is an inflammatory disorder of the placenta that commonly precedes preterm delivery. Preterm birth related to chorioamnionitis and fetal inflammation has been associated with a risk for serious inflammatory complications in infancy. In addition, preterm infants exposed to chorioamnionitis may be more susceptible to infection in the neonatal intensive care unit and possibly later in life. A significant body of work has established an association between chorioamnionitis and inflammatory processes. However, the potential consequences of this inflammation on postnatal immunity are less understood. In this review, we will discuss current knowledge regarding the effects of fetal exposure to inflammation on postnatal immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prenatal Endotoxin Exposure Induces Fetal and Neonatal Renal Inflammation via Innate and Th1 Immune Activation in Preterm Pigs.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 30;11:565484. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.565484. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193334 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of S100A Alarmins in Cord Blood Monocytes Is Highly Associated With Chorioamnionitis and Fetal Inflammation in Preterm Infants.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 16;11:1194. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01194. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32612607 Free PMC article.
-
Preterm Birth Is Associated With Immune Dysregulation Which Persists in Infants Exposed to Histologic Chorioamnionitis.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 27;12:722489. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.722489. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34512648 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Histological and Clinical Chorioamnionitis With Neonatal Sepsis Among Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 5;11:972. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00972. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582153 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-induced immune suppression of the fetus: a potential link between chorioamnionitis and postnatal early onset sepsis.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 Apr;25 Suppl 1:8-11. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2012.664447. Epub 2012 Mar 2. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012. PMID: 22348330 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Intrauterine Inflammation, Delivery, and Postnatal Feeding on the Temporal Changes of Serum Alpha 1 Acid Glycoprotein Levels in Extremely-Low-Birth-Weight Infants.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 4;14(23):5162. doi: 10.3390/nu14235162. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501194 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of In Utero Exposure to Maternal Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Immunomodulators on Infant Immune System Development and Function.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;16(1):165-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.03.005. Epub 2023 Mar 25. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36972763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timing of Maternal Stress Differentially Affects Immune and Stress Phenotypes in Progeny.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 25;14(21):3074. doi: 10.3390/ani14213074. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518797 Free PMC article.
-
Mild/asymptomatic COVID-19 in unvaccinated pregnant mothers impairs neonatal immune responses.JCI Insight. 2023 Sep 12;8(19):e172658. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.172658. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37698937 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of multipotent adult progenitor cells modulates the systemic and cerebral immune response in an ovine model of chorioamnionitis.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 May 2;23:100458. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100458. eCollection 2022 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 35647567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Redline RW. Inflammatory response in acute chorioamnionitis. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;17:20–25 - PubMed
-
- Peng CC, Chang JH, Lin HY, Cheng PJ, Su BH. Intrauterine inflammation, infection, or both (Triple I): A new concept for chorioamnionitis. Pediatr Neonatol 2018;59:231–237 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki S Association between clinical chorioamnionitis and histological funisitis at term. J Neonatal Perinatal Med 2019;12:37–40 - PubMed
-
- Lahra MM, Jeffery HE. A fetal response to chorioamnionitis is associated with early survival after preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190:147–151 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

