Genome-Wide Association Study of Diabetic Kidney Disease Highlights Biology Involved in Glomerular Basement Membrane Collagen
- PMID: 31537649
- PMCID: PMC6779358
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019030218
Genome-Wide Association Study of Diabetic Kidney Disease Highlights Biology Involved in Glomerular Basement Membrane Collagen
Abstract
Background: Although diabetic kidney disease demonstrates both familial clustering and single nucleotide polymorphism heritability, the specific genetic factors influencing risk remain largely unknown.
Methods: To identify genetic variants predisposing to diabetic kidney disease, we performed genome-wide association study (GWAS) analyses. Through collaboration with the Diabetes Nephropathy Collaborative Research Initiative, we assembled a large collection of type 1 diabetes cohorts with harmonized diabetic kidney disease phenotypes. We used a spectrum of ten diabetic kidney disease definitions based on albuminuria and renal function.
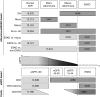
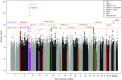
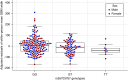
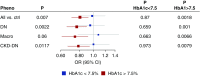
Results: Our GWAS meta-analysis included association results for up to 19,406 individuals of European descent with type 1 diabetes. We identified 16 genome-wide significant risk loci. The variant with the strongest association (rs55703767) is a common missense mutation in the collagen type IV alpha 3 chain (COL4A3) gene, which encodes a major structural component of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM). Mutations in COL4A3 are implicated in heritable nephropathies, including the progressive inherited nephropathy Alport syndrome. The rs55703767 minor allele (Asp326Tyr) is protective against several definitions of diabetic kidney disease, including albuminuria and ESKD, and demonstrated a significant association with GBM width; protective allele carriers had thinner GBM before any signs of kidney disease, and its effect was dependent on glycemia. Three other loci are in or near genes with known or suggestive involvement in this condition (BMP7) or renal biology (COLEC11 and DDR1).
Conclusions: The 16 diabetic kidney disease-associated loci may provide novel insights into the pathogenesis of this condition and help identify potential biologic targets for prevention and treatment.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic nephropathy; end-stage renal disease; genetic renal disease; human genetics; kidney disease.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Biologic Underpinnings of Type 1 Diabetic Kidney Disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Oct;30(10):1782-1783. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019080803. Epub 2019 Sep 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31570541 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Type IV collagen and diabetic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Jan;16(1):3-4. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0229-1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31728033 No abstract available.
-
Hypothesis as to How a Common Missense Mutation in COL4A3 May Confer Protection against Diabetic Kidney Disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Mar;31(3):663-664. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019090966. Epub 2020 Jan 27. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31988270 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention : National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017 Estimates of Diabetes and its Burden in the United States Background, Atlanta, GA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services, 2017
-
- Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J, et al. .: Diabetic kidney disease: A report from an ADA Consensus conference. Am J Kidney Dis 64: 510–533, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Krolewski M, Eggers PW, Warram JH: Magnitude of end-stage renal disease in IDDM: A 35 year follow-up study. Kidney Int 50: 2041–2046, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Harjutsalo V, Katoh S, Sarti C, Tajima N, Tuomilehto J: Population-based assessment of familial clustering of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 53: 2449–2454, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Quinn M, Angelico MC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS: Familial factors determine the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with IDDM. Diabetologia 39: 940–945, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EY016379/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15025/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K12 DK094721/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK110919/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R37 DK034818/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 098381/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK034818/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK110550/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK094176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK094157/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK081943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL122515/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

