Novel Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System and Associated Peptides in Hypertension and Heart Failure
- PMID: 31537750
- PMCID: PMC6782023
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.118.017129
Novel Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System and Associated Peptides in Hypertension and Heart Failure
Abstract
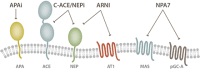
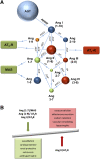
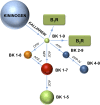
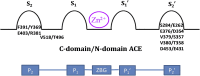
Despite the success of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) blockers, current therapies for hypertension and related cardiovascular diseases are still inadequate. Identification of additional components of the RAS and associated vasoactive pathways, as well as new structural and functional insights into established targets, have led to novel therapeutic approaches with the potential to provide improved cardiovascular protection and better blood pressure control and/or reduced adverse side effects. The simultaneous modulation of several neurohumoral mediators in key interconnected blood pressure-regulating pathways has been an attractive approach to improve treatment efficacy, and several novel approaches involve combination therapy or dual-acting agents. In addition, increased understanding of the complexity of the RAS has led to novel approaches aimed at upregulating the ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas axis to counter-regulate the harmful effects of the ACE/angiotensin II/angiotensin III/AT1R axis. These advances have opened new avenues for the development of novel drugs targeting the RAS to better treat hypertension and heart failure. Here we focus on new therapies in preclinical and early clinical stages of development, including novel small molecule inhibitors and receptor agonists/antagonists, less conventional strategies such as gene therapy to suppress angiotensinogen at the RNA level, recombinant ACE2 protein, and novel bispecific designer peptides.
Copyright © 2019 by The Author(s).
Figures


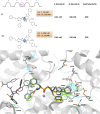
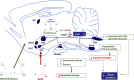
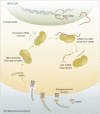
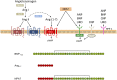
References
-
- Abassi Z, Karram T, Ellaham S, Winaver J, Hoffman A. (2004) Implications of the natriuretic peptide system in the pathogenesis of heart failure: diagnostic and therapeutic importance. Pharmacol Ther 102:223–241. - PubMed
-
- AbdAlla S, Lother H, Abdel-tawab AM, Quitterer U. (2001) The angiotensin II AT2 receptor is an AT1 receptor antagonist. J Biol Chem 276:39721–39726. - PubMed
-
- AbdAlla S, Lother H, Quitterer U. (2000) AT1-receptor heterodimers show enhanced G-protein activation and altered receptor sequestration. Nature 407:94–98. - PubMed
-
- Agah R, Bandi V, Guntupalli KK. (1997) Angioedema: the role of ACE inhibitors and factors associated with poor clinical outcome. Intensive Care Med 23:793–796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

