Evaluation of isosorbide-5-mononitrate as a cervical ripening agent prior to induced abortion in contrast to misoprostol- a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31538074
- PMCID: PMC6737056
- DOI: 10.5468/ogs.2019.62.5.313
Evaluation of isosorbide-5-mononitrate as a cervical ripening agent prior to induced abortion in contrast to misoprostol- a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether vaginal application of 40 mg isosorbide-5-mononitrate (ISMN) has a comparable cervical ripening efficacy to and lesser side effects than 400 µg misoprostol in women scheduled for the first trimester induced abortion using a manual vacuum aspirator (MVA).
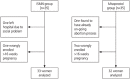
Methods: We conducted a prospective randomized open-label study in 70 women at 6-12 weeks of pregnancy at the R G Kar Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata, India, over a period of two years from 2015 to 2017. Forty milligrams of ISMN and 400 µg misoprostol were vaginally applied for cervical priming. The primary outcome measure was the cervical response assessed by the passage of the appropriate and largest sized MVA cannula through the internal os without resistance, at the beginning of the procedure.
Results: The base line cervical dilatation was found to be significantly higher in the misoprostol group than in the ISMN group (7.65±1.38 vs. 6.9±1.26 mm; P=0.025, 95% confidence interval, -1.4046 to -0.953). However, when the women were sub-analyzed based on parity, there was no statistically significant difference in the same parameters among the multigravid women. The need for further cervical dilatation was significantly higher in the ISMN group when the primigravid women were compared, although the multigravid women responded favorably to ISMN.
Conclusion: In the primigravid women, misoprostol appears to exert a higher efficacy as a cervical ripening agent in contrast to ISMN. However, ISMN can be used in multigravid women for the same purpose as in this group, misoprostol did not show any significant improvement in efficacy over ISMN.
Keywords: Cervical ripening; Induced abortion; Isosorbide-5-mononitrate.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers' bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Pandve HT. Health-related Millennium Development Goals: how much India has progressed? Arch Med Health Sci. 2015;3:335–339.
-
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, Tunçalp Ö, Moller AB, Daniels J, et al. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2:e323–33. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India. A strategic approach to Reproductive, Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A) in India. New Delhi: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India; 2013.
-
- Li CF, Chan CW, Ho PC. A study of the efficacy of cervical ripening with nitric oxide donor versus placebo for cervical priming before second-trimester termination of pregnancy. Contraception. 2003;68:269–272. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources