One-Year Outcomes of Second-Generation Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stents (iStent Inject) Implantation with Cataract Surgery in Different Glaucoma Subtypes and Severities
- PMID: 31538316
- PMCID: PMC6858422
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-019-00214-z
One-Year Outcomes of Second-Generation Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stents (iStent Inject) Implantation with Cataract Surgery in Different Glaucoma Subtypes and Severities
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the 1-year efficacy and safety of the implantation of two second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents (iStent Inject®) with concomitant cataract surgery in various subtypes and severities of glaucoma.
Methods: This single-surgeon, consecutive case series from a Canadian academic ophthalmology center included subjects with cataract, glaucoma, and the need to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) and/or medications. The 12-month outcomes included mean IOP and medication burden as well as the proportions of eyes with IOP ≤ 18, ≤ 15, and ≤ 12 mmHg compared to baseline. Other measures included corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA), cup-to-disc ratio (CDR), visual field mean deviation (VF MD), retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness, ganglion cell inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) thickness, and adverse events.
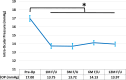
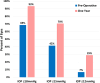
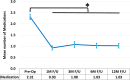
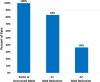
Results: In 118 eyes, mean IOP reduced from 17.00 ± 3.82 mmHg preoperatively to 13.97 ± 2.65 mmHg at the 12-month follow-up mark (17.8% reduction, p < 0.001), and mean medication burden decreased from 2.31 ± 1.33 preoperatively to 1.03 ± 1.10 medications (56% reduction, p < 0.001). After 12 months, 93% of eyes achieved IOP ≤ 18 mmHg (versus 69% preoperatively), 70% of eyes achieved IOP ≤ 15 mmHg (versus 42% preoperatively), and 29% of eyes achieved IOP ≤ 12 mmHg (versus 7% preoperatively). For all eyes, topical medications were either maintained or decreased from baseline, with ≥ 1 medication eliminated from the preoperative regimen for 83% of eyes and ≥ 2 medications eliminated for 36% of eyes. Visual acuity improved significantly, consistent with expectations for cataract surgery, while CDR, VF MD, and RNFL and GCIPL thicknesses remained stable. Safety was favorable, with no intraoperative complications and few transient adverse events postoperatively.
Conclusion: iStent Inject implantation with cataract surgery safely reduced IOP and medication burden in a real-world clinical population with mild to severe glaucoma, and stabilized visual field, as well as RNFL and GCIPL thicknesses on OCT.
Funding: The Rapid Service Fees were funded by Glaukos Corporation.
Keywords: Cataract; Glaucoma; Micro-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS); Stent; Trabecular micro-bypass; iStent Inject.
Conflict of interest statement
Paul Harasymowycz is consultant for Allergan, Glaukos, Ivantis, J and J Vision, Santen. Ali Salimi and Julie Lapointe have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three-Year Outcomes of Second-generation Trabecular Micro-bypass Stents (iStent inject) With Phacoemulsification in Various Glaucoma Subtypes and Severities.J Glaucoma. 2021 Mar 1;30(3):266-275. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000001716. J Glaucoma. 2021. PMID: 33105306
-
Real-world Case Series of iStent or iStent inject Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stents Combined with Cataract Surgery.Ophthalmol Ther. 2019 Dec;8(4):549-561. doi: 10.1007/s40123-019-00208-x. Epub 2019 Aug 17. Ophthalmol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31422555 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective, Non-randomized, 36-Month Study of Second-Generation Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stents with Phacoemulsification in Eyes with Various Types of Glaucoma.Ophthalmol Ther. 2018 Dec;7(2):405-415. doi: 10.1007/s40123-018-0152-8. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Ophthalmol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30430427 Free PMC article.
-
Ab interno trabecular bypass surgery with Schlemm´s canal microstent (Hydrus) for open angle glaucoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 9;3(3):CD012740. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012740.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32147807 Free PMC article.
-
Standalone iStent Trabecular Micro-bypass Glaucoma Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Glaucoma. 2021 Jul 1;30(7):606-620. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000001805. J Glaucoma. 2021. PMID: 33596009
Cited by
-
Chronic Granulomatous Inflammation after CyPass® Implantation.Ocul Oncol Pathol. 2020 Aug;6(4):259-264. doi: 10.1159/000505491. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Ocul Oncol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33005615 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of oral anticoagulation on success rates and risk of bleeding events after iStent inject implantation combined with phacoemulsification.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov;258(11):2483-2487. doi: 10.1007/s00417-020-04894-3. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32816101 Free PMC article.
-
iStent versus iStent inject implantation combined with phacoemulsification in open angle glaucoma.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep;69(9):2488-2495. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_308_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34427250 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery: Safety of Individual Devices.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):6833. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226833. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined microinvasive glaucoma surgery in osteogenesis imperfecta patient with refractory open angle glaucoma.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2020 Feb 5;18:100617. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2020.100617. eCollection 2020 Jun. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32083228 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

