Early Diagnosis of Tularemia by Flow Cytometry, Czech Republic, 2003-20151
- PMID: 31538915
- PMCID: PMC6759275
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2510.181875
Early Diagnosis of Tularemia by Flow Cytometry, Czech Republic, 2003-20151
Abstract
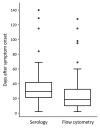
We retrospectively assessed the utility of a flow cytometry-based test quantifying the percentage of CD3+ T cells with the CD4-/CD8- phenotype for predicting tularemia diagnoses in 64 probable and confirmed tularemia patients treated during 2003-2015 and 342 controls with tularemia-like illnesses treated during 2012-2015 in the Czech Republic. The median percentage of CD3+/CD4-/CD8- T cells in peripheral blood was higher in tularemia patients (19%, 95% CI 17%-22%) than in controls (3%, 95% CI 2%-3%). When we used 8% as the cutoff, this test's sensitivity was 0.953 and specificity 0.895 for distinguishing cases from controls. The CD3+/CD4-/CD8- T cells increased a median of 7 days before tularemia serologic test results became positive. This test supports early presumptive diagnosis of tularemia for clinically suspected cases 7-14 days before diagnosis can be confirmed by serologic testing in regions with low prevalences of tularemia-like illnesses.
Keywords: Czech Republic; Francisella tularensis; ROC curve; T cells; bacteria; diagnosis; double-negative T cells; early diagnosis; flow cytometry; gamma delta T cells; intracellular pathogens; peripheral blood; tularemia; work-up; γδ T cells.
Figures

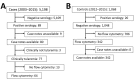
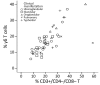
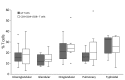

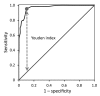
References
-
- McCoy GW, Chapin CW. Further observations on a plague-like disease of rodents with a preliminary note on the causative agent, Bacterium tularense. J Infect Dis. 1912;10:61–72. 10.1093/infdis/10.1.61 - DOI
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Tularaemia-annual epidemiological report 2016. 2019. Jan 22 [cited 2018 Dec 7]. https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/documents/AER_for_2016-tularae...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

