Neonatal infant EEG bursts are altered by prenatal maternal depression and serotonin selective reuptake inhibitor use
- PMID: 31539768
- PMCID: PMC6944195
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.08.021
Neonatal infant EEG bursts are altered by prenatal maternal depression and serotonin selective reuptake inhibitor use
Abstract
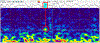
Objective: Increasingly, serotonin selective reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) medications are prescribed in pregnancy. These medications pass freely into the developing fetus but little is known about their effect on brain development in humans. In this study we determine if prenatal maternal depression and SSRI medication change the EEG infant delta brush bursts which are an early marker of normal brain maturation.
Methods: We measured delta brush bursts from the term infants of three groups of mothers (controls (N = 52), depressed untreated (N = 15), and those taking serotonin SSRI medication (N = 10). High density EEGs were obtained during sleep at an average age of 44 weeks post conceptional age. We measured the rate of occurrence, brush amplitude, oscillation frequency and duration of the bursts.
Results: Compared to infants of control mothers, the parameters of delta brush bursts of the offspring of depressed and SSRI-using mothers are significantly altered: burst amplitude is decreased; the oscillation frequency increased, and the duration increased (SSRI only). These significant differences were found during both sleep states.
Conclusions: Electrocortical bursting activity (i.e. delta brushes) is known to play an important role in early central nervous system (CNS) synaptic formation and function.
Significance: Maternal depression or SSRI use may alter brain function in their offspring.
Keywords: Delta brush; EEG burst; Infant EEG; Prenatal maternal depression; SSRI.
Copyright © 2019 International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
None of the authors have potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

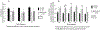
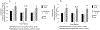
References
-
- Akhmetshina D, Zakharov A, Vinokurova D, Nasretdinov A, Valeeva G, Khazipov R. The serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram suppresses activity in the neonatal rat barrel cortex in vivo. Brain Res Bul 2016;124:48–54. - PubMed
-
- André M, Lamblin MD, d’Allest AM, Curzi-Dascalova L, Moussalli-Salefranque F, Nguyen Thetich S, et al. Electroencephalography in premature and full-term infants. Developmental features and glossary. Neurophysiol Clin 2010;40(2):59–124. - PubMed
-
- Ansorge MS, Zhou M, Lira A, Hen R, Gingrich JA. Early-life blockade of the 5-HT transporter alters emotional behavior in adult mice. Science 2004;306 (5697):879–81. - PubMed
-
- Barnes NM, Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function.Neuropharm 1999;38(8):1083–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

